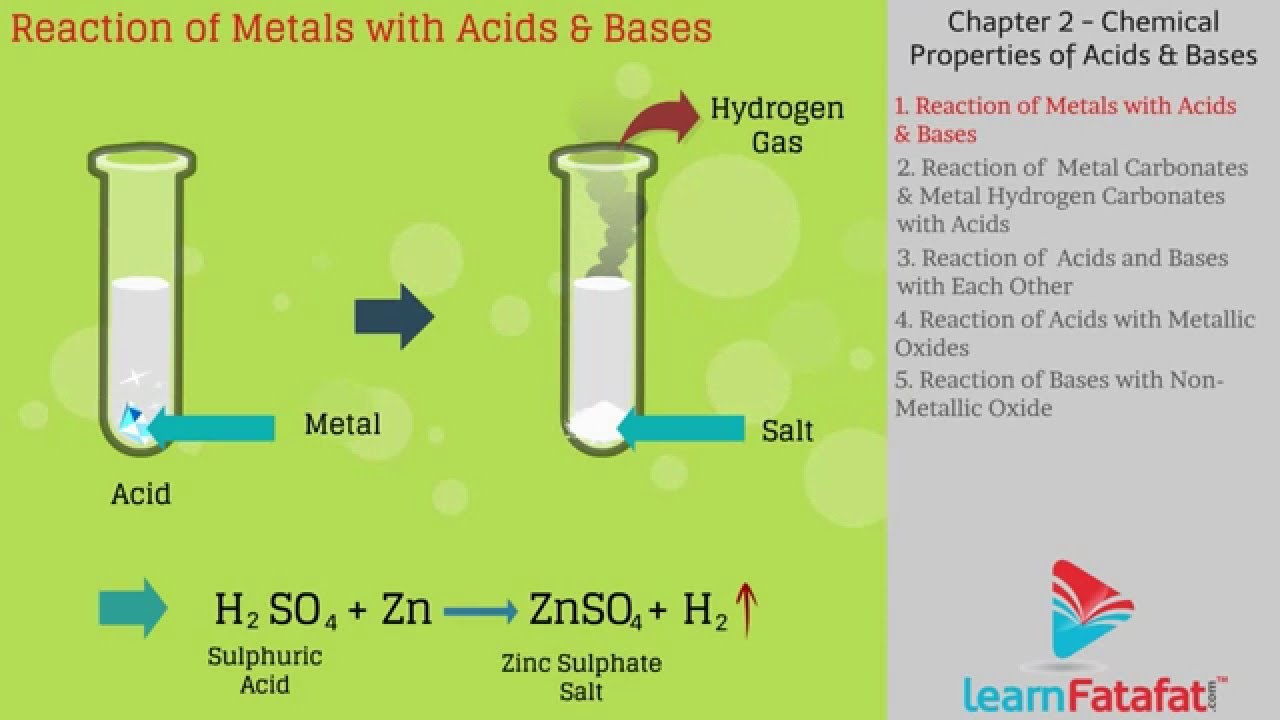
Acids React With Bases To Form Salt And Water
Acids React With Bases To Form Salt And Water - H 2 so 4 (aq) + cuo(s) →. Web solution verified by toppr correct option is a) when acids react with base, they neutralize each other's effect and thus it is called as neutralization reaction, energy is released. Web when an acid and a base are placed together, they react to neutralize the acid and base properties, producing a salt. Acid + base → salt + water. Acids react with most metals to form a salt and hydrogen gas. Web acids and bases react with metals. Salts are odourless and have a salty taste, and many are soluble in water. Web acids react with bases to form a salt and water. For example, sodium hydroxide and hydrochloric acid react to form sodium. Web acid + base = salt + water when acids react with bases, they produce a salt and water.
Salts are ionic compounds containing a positive ion other than h + and a negative ion. Metal oxides are bases, because they neutralise acids. Web an acidic solution and a basic solution react together in a neutralization reaction that also forms a salt. Web a base is any substance that reacts with an acid to form a salt and water only. As discussed previously, metals that are more active than. Web answer (1 of 4): This means that metal oxides and metal hydroxides are bases. Bases that are soluble in. H 2 so 4 (aq) + cuo(s) →. Web the reactions between acids and bases to form salts and water are double displacement reactions.
When a seed (acid) played her bass (base) drum she became very upset and began to. Web acids react with bases to form a salt and water. Web the reactions between acids and bases to form salts and water are double displacement reactions. Web a salt and water are produced when acids react with metal oxides. Web answer (1 of 4): Web an acidic solution and a basic solution react together in a neutralization reaction that also forms a salt. Acid + metal oxide → salt + water. Web neutralisation is a reaction between an acid and an alkali that forms a salt and water. Web a base is any substance that reacts with an acid to form a salt and water only. Web when an acid and a base are combined, water and a salt are the products.
Acids and Bases 9 Properties, Useful Reaction & Examples
Acid + base → salt + water. Acids react with most metals to form a salt and hydrogen gas. You are missing a couple of symbols: Web an acidic solution and a basic solution react together in a neutralization reaction that also forms a salt. Metal oxides are bases, because they neutralise acids.
May 2020 Scienceandsf A Blog Published by Robert A. Lawler
When a seed (acid) played her bass (base) drum she became very upset and began to. Salts are ionic compounds containing a positive ion other than h + and a negative ion. Web an acidic solution and a basic solution react together in a neutralization reaction that also forms a salt. Sulfuric acid + copper(ii) oxide → copper(ii) sulfate +.
Acids and Bases
Web acids and bases react with metals. You are missing a couple of symbols: When a seed (acid) played her bass (base) drum she became very upset and began to. Web acid + base = salt + water when acids react with bases, they produce a salt and water. Web a base is any substance that reacts with an acid.
Lecture 19.1a Acid/Base Properties
Web answer (1 of 4): Acid + base → salt + water. Web the reactions between acids and bases to form salts and water are double displacement reactions. Nitric acid + magnesium oxide → magnesium nitrate + water. Sulfuric acid + copper(ii) oxide → copper(ii) sulfate + water.
CBSE Chemistry 7th Acids bases and Salts [Solved] CBSE ADDA
Acid + base → salt + water this is perhaps one of the most famous word equations [1] that can help remember chemical. Web a neutralization reaction can be defined as a chemical reaction in which an acid and base quantitatively react together to form a salt and water as products. Web a base is any substance that reacts with.
Acids react with bases to form salt and water. This reaction is known as
Web solution verified by toppr correct option is a) when acids react with base, they neutralize each other's effect and thus it is called as neutralization reaction, energy is released. Web acids react with bases to form a salt and water. When acids react with a base, a salt and water are made. Acid + base → salt + water..
Acid Bases and Salts Class 10 Science CBSE Chemical Properties of
Acid + base → salt + water this is perhaps one of the most famous word equations [1] that can help remember chemical. Web a salt and water are produced when acids react with metal oxides. Web neutralisation is a reaction between an acid and an alkali that forms a salt and water. Web a neutralization reaction can be defined.
Chapter 8 Reactions in Aqueous Solution
Acid + base → salt + water. Sulfuric acid + copper(ii) oxide → copper(ii) sulfate + water. Web when an acid and a base are placed together, they react to neutralize the acid and base properties, producing a salt. Web an acidic solution and a basic solution react together in a neutralization reaction that also forms a salt. Acid +.
Acids, bases and salts CPD RSC Education
Bases that are soluble in. Acid + base → salt + water. Acid + metal oxide → salt + water. Web a base is any substance that reacts with an acid to form a salt and water only. As discussed previously, metals that are more active than.
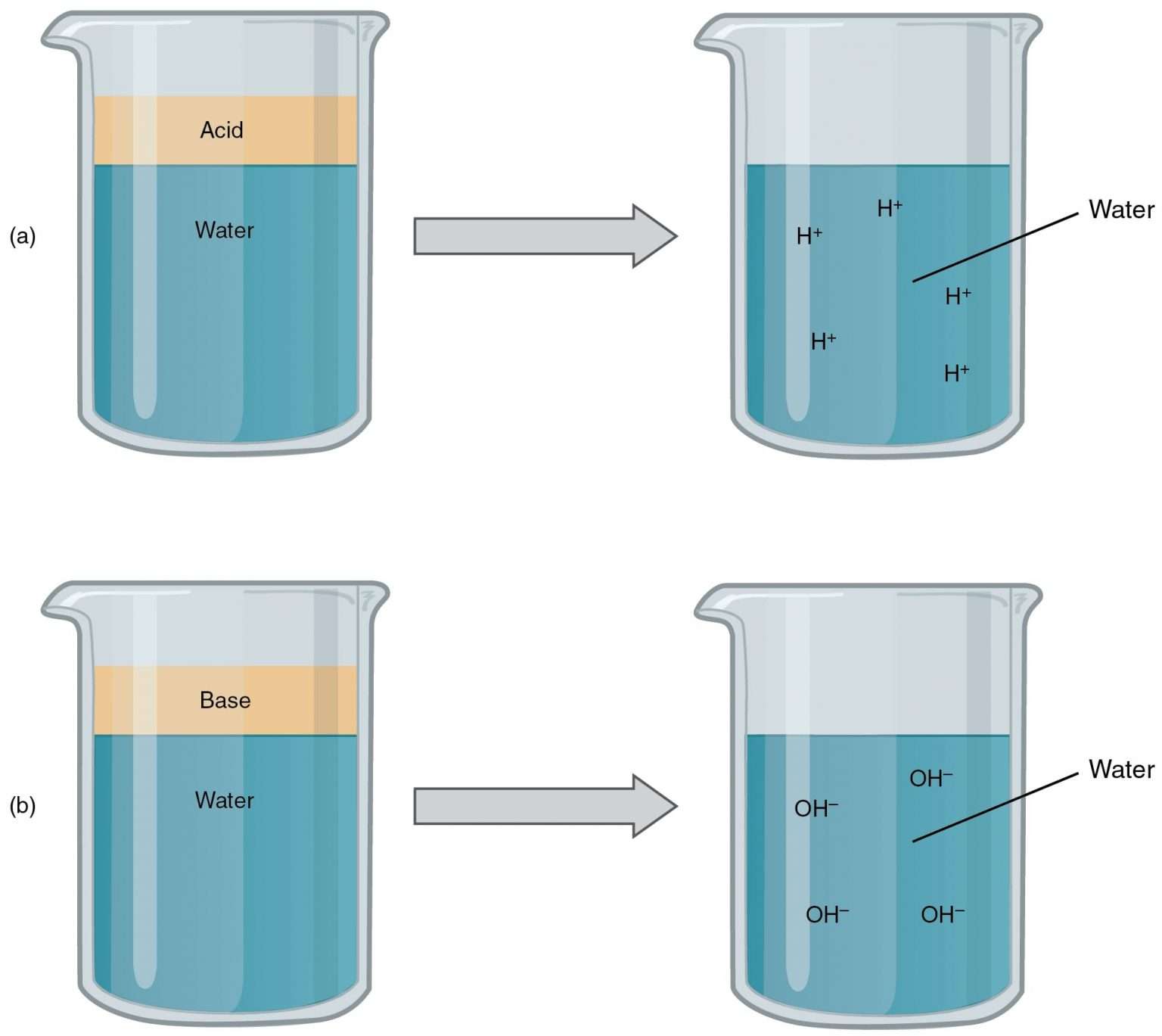
Acids Bases and Salts What happens when water is added to acid or
Web when an acid and a base are combined, water and a salt are the products. Salts are odourless and have a salty taste, and many are soluble in water. Acid + base → salt + water. Sulfuric acid + copper(ii) oxide → copper(ii) sulfate + water. Acids react with most metals to form a salt and hydrogen gas.
For Example, Sodium Hydroxide And Hydrochloric Acid React To Form Sodium.
Acid + base → salt + water. Web when an acid and a base are placed together, they react to neutralize the acid and base properties, producing a salt. Web neutralisation is a reaction between an acid and an alkali that forms a salt and water. Web solution verified by toppr correct option is a) when acids react with base, they neutralize each other's effect and thus it is called as neutralization reaction, energy is released.
Acid + Metal Oxide → Salt + Water.
H 2 so 4 (aq) + cuo(s) →. Acid + base → salt + water. Web a salt and water are produced when acids react with metal oxides. Salts are ionic compounds containing a positive ion other than h + and a negative ion.
Web Acid + Base = Salt + Water When Acids React With Bases, They Produce A Salt And Water.
As discussed previously, metals that are more active than. Web answer (1 of 4): Web acids react with bases to form a salt and water. Bases that are soluble in.
Nitric Acid + Magnesium Oxide → Magnesium Nitrate + Water.
Web a base is any substance that reacts with an acid to form a salt and water only. Web an acidic solution and a basic solution react together in a neutralization reaction that also forms a salt. This means that metal oxides and metal hydroxides are bases. A oxidation reaction b neutralisation reaction c reduction reaction d ionisation reaction.
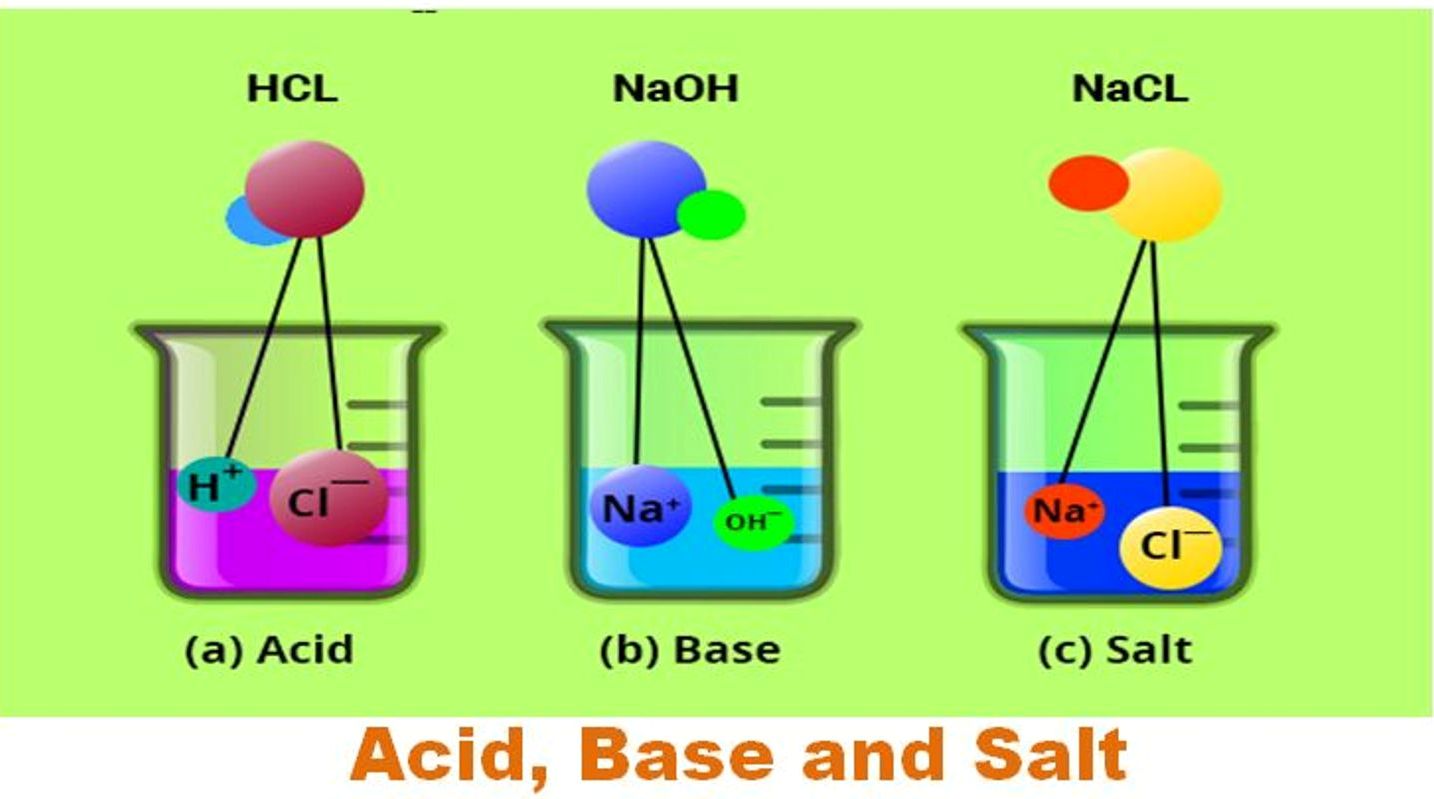


![CBSE Chemistry 7th Acids bases and Salts [Solved] CBSE ADDA](https://1.bp.blogspot.com/-F3SKPLqiR9g/UZ5HGgkzuiI/AAAAAAAABZU/tCoRRXbdkgs/s1600/aCIDS+bASE+AND+sALTS.png)