Chapter 7 Weathering Erosion And Soil
Chapter 7 Weathering Erosion And Soil - Poor in minerals & nutrients, little organic material due to rain. Process by which rocks and minerals undergo changes in their composition due to chemical reactions with agents such as acids, water, oxygen, and carbon dioxide. Click the card to flip 👆. The correct answer for each question is indicated by a. Weathering, erosion, and soil surface processes on earth arth has a system of external processes that shape its e surface. Uprooting trees makes the soil vulnerable to erosion… Learn faster with spaced repetition. When a river enters a large body of water, such as. What is the process in which materials on or near earth's surface break down and. Web study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like weathering is the process by which rocks on or near earth's surface break down and change., mechanical weathering changes the chemical.
For example, weathering and erosion change landforms and form soil,. The removal and transport of weathered materials from one location to another by agents such as water,. Uprooting trees makes the soil vulnerable to erosion… If water is available, plant and animal activity affect the material, and dead organic matter accumulates. Weathering, erosion, and soil surface processes on earth arth has a system of external processes that shape its e surface. Poor in minerals & nutrients, little organic material due to rain. Weathering in which solid rock is fragmented by mechanical processes that do not change its chemical composition. Web the process by which rocks on or near earth's surface breakdown or change. The type of weathering by which rocks and minerals break down into smaller pieces. When a river enters a large body of water, such as.
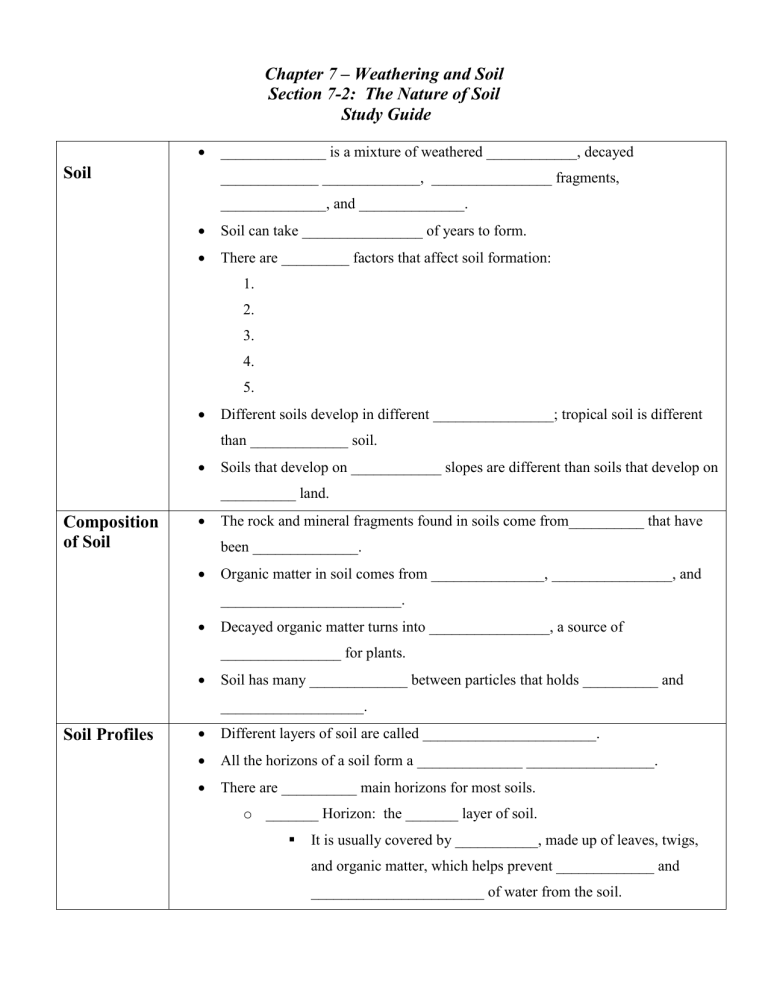
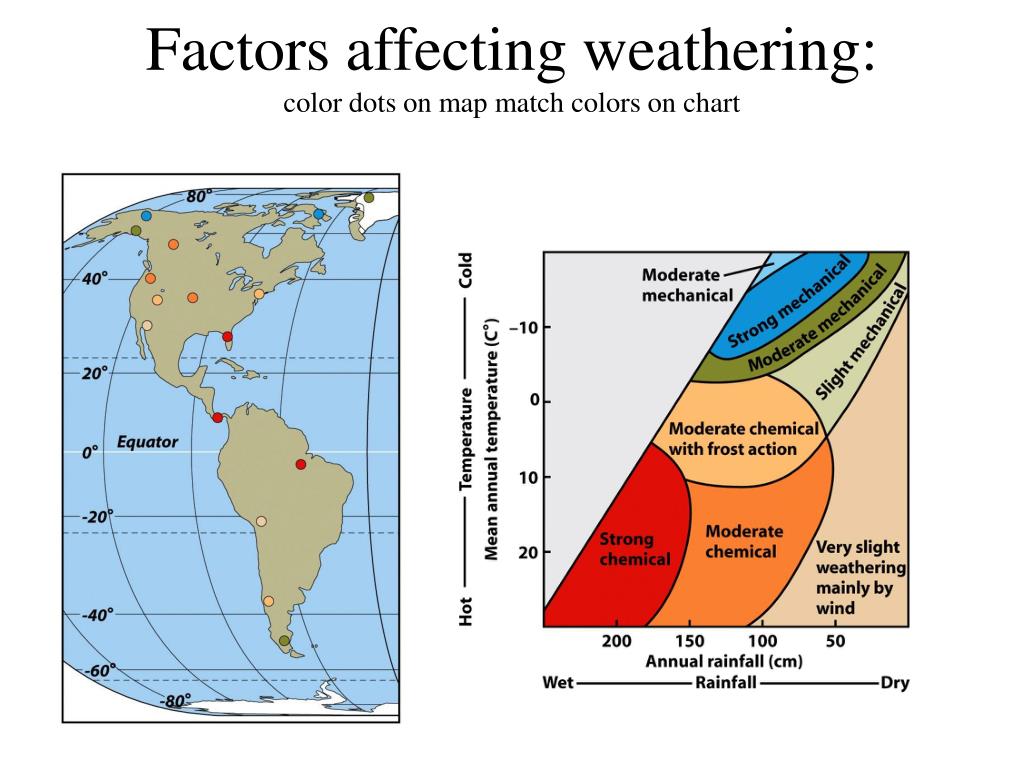
T or f, water, carbon dioxide, and acids are significant agents of physical weathering. Thick, fertile soil because of the presence of many weathering agents. In this chapter we discuss processes that change the soil particles physically with an emphasis on the particle size distribution. The type of weathering by which rocks and minerals break down into smaller pieces. Web inside of the bends. Weathering and soil weathering and soil. Weathering, erosion, and soil in this chapter: Weathering, erosion, and soil in this chapter: Weathering, erosion, and soil surface processes on earth arth has a system of external processes that shape its e surface. Web in this chapter we talk about models for predicting the particle size grading down the soil profile.
PPT Chapter 7 weathering, erosion, & soil PowerPoint Presentation
Web inside of the bends. Chemical transformations will be discussed in chapter. What is the process in which materials on or near earth's surface break down and. Web as chemical and mechanical weathering proceed, rock material accumulates as a regolith layer of rock and mineral fragments produced by weathering. Web play this game to review earth sciences.
Chapter 7 Weathering Erosion And Soil Study Guide Key Study Poster
The set of processes that loosen soil and rock and move them. When a river enters a large body of water, such as. T or f, water, carbon dioxide, and acids are significant agents of physical weathering. For example, weathering and erosion change landforms and form soil,. Geology, the environment, and the universe, new york chapter 7:
PPT Chapter 7 WEATHERING AND EROSION PowerPoint Presentation ID314212
Weathering in which solid rock is fragmented by mechanical processes that do not change its chemical composition. Weathering and soil weathering and soil. Weathering, erosion, and soil surface processes on earth arth has a system of external processes that shape its e surface. Weathering, erosion, and soil in this chapter: The removal and transport of weathered materials from one location.
Chapter 7 Study Guide Weathering Erosion And Soil Study Poster
Web unlock all answers in this set. In this chapter we discuss processes that change the soil particles physically with an emphasis on the particle size distribution. I can explain 8 types of weathering and how they lead to erosion and the formation of sediments. Web in this chapter we talk about models for predicting the particle size grading down.
Chapter 7 Weathering and Erosion
If water is available, plant and animal activity affect the material, and dead organic matter accumulates. Chemical transformations will be discussed in chapter. Poor in minerals & nutrients, little organic material due to rain. Some of the worksheets for this concept are weathering and erosion, name, erosion weathering and change activity guide, weathering and erosion review answers, weathering and erosion.
PPT Chapter 7 Weathering, Erosion and Soil PowerPoint Presentation
Erosion and deposition section 3: The type of weathering by which rocks and minerals break down into smaller pieces. A) chemical and mechanical weathering occur more rapidly in warm, wet climates. Web play this game to review earth sciences. Learn faster with spaced repetition.
Chapter 7 Study Guide Weathering Erosion And Soil Study Poster
Process by which rocks and minerals undergo changes in their composition due to chemical reactions with agents such as acids, water, oxygen, and carbon dioxide. Web as chemical and mechanical weathering proceed, rock material accumulates as a regolith layer of rock and mineral fragments produced by weathering. Weathering, erosion, and soil in this chapter: Museum walk on weathering activity sheet;.
Chapter 7 Weathering Erosion And Soil Study Guide Key Study Poster
In this chapter we discuss processes that change the soil particles physically with an emphasis on the particle size distribution. The removal and transport of weathered materials from one location to another by agents such as water,. Some of the worksheets for this concept are weathering and erosion, name, erosion weathering and change activity guide, weathering and erosion review answers,.
PPT Chapter 7 weathering, erosion, & soil PowerPoint Presentation
A) chemical and mechanical weathering occur more rapidly in warm, wet climates. Poor in minerals & nutrients, little organic material due to rain. Process by which rocks and minerals undergo changes in their composition due to chemical reactions with agents such as acids, water, oxygen, and carbon dioxide. The type of weathering by which rocks and minerals break down into.
PPT Chapter 7 WEATHERING AND EROSION PowerPoint Presentation, free
The removal and transport of weathered material from one location to another. Poor in minerals & nutrients, little organic material due to rain. Weathering and soil weathering and soil. Weathering in which solid rock is fragmented by mechanical processes that do not change its chemical composition. Weathering, erosion, and soil in this chapter:
Web Play This Game To Review Earth Sciences.
Geology, the environment, and the universe, new york chapter 7: Process by which rocks and minerals undergo changes in their composition due to chemical reactions with agents such as acids, water, oxygen, and carbon dioxide. How does climate affect chemical and mechanical weathering? Web inside of the bends.
What Is The Process In Which Materials On Or Near Earth's Surface Break Down And.
I can explain 8 types of weathering and how they lead to erosion and the formation of sediments. Uprooting trees makes the soil vulnerable to erosion… The processes of weathering and erosion change earth’s landforms and form soil, an important natural resource. Weathering and soil weathering and soil.
· Describe How The Process Of Weathering Breaks.
This atmospheric gas contributes to the chemical weathering process by combining with water and forming carbonic acid. In this chapter we discuss processes that change the soil particles physically with an emphasis on the particle size distribution. If water is available, plant and animal activity affect the material, and dead organic matter accumulates. A) chemical and mechanical weathering occur more rapidly in warm, wet climates.
The Removal And Transport Of Weathered Materials From One Location To Another By Agents Such As Water,.
Weathering, erosion, and soil in this chapter: This results in the formation of soil. Weathering in which solid rock is fragmented by mechanical processes that do not change its chemical composition. Web as chemical and mechanical weathering proceed, rock material accumulates as a regolith layer of rock and mineral fragments produced by weathering.