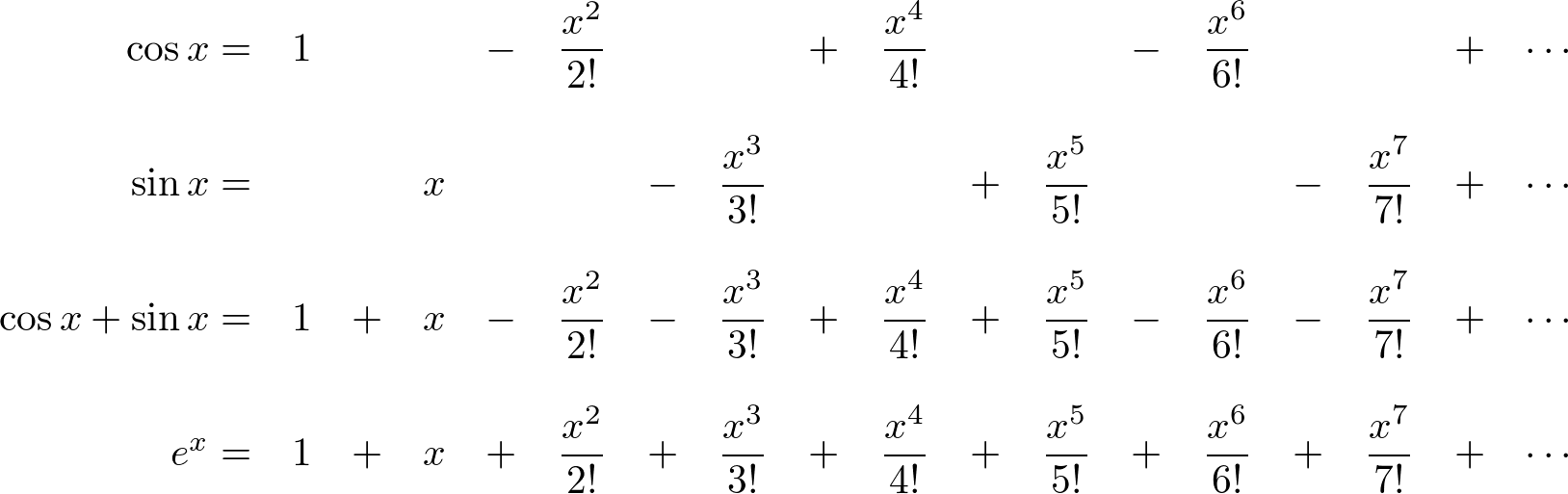Exponential Form Of Sin
Exponential Form Of Sin - Web according to euler, we should regard the complex exponential eit as related to the trigonometric functions cos(t) and sin(t) via the following inspired definition: Web #1 dough 19 0 hi, my question is from modern engineering mathematics by glyn james pg 177 # 17a using the exponential forms of cos (theta) and sin (theta). Web in physics, a sinusoidal (or monochromatic) plane wave is a special case of plane wave: E^x = sum_(n=0)^oo x^n/(n!) so: E x = ∑ (k=0 to ∞) (x k / k!) = 1 + x + (x 2 / 2!) + (x 3 / 3!) +. E jx = cos (x) + jsin (x) and the exponential representations of sin & cos, which are derived from euler's formula: What is going on, is that electrical engineers tend to ignore the fact that one needs to add or subtract the complex. Eit = cos t + i. (45) (46) (47) from these relations and the properties of exponential multiplication you can painlessly prove all. Web exponentials the exponential of a real number x, written e x or exp(x), is defined by an infinite series,.
Web exponentials the exponential of a real number x, written e x or exp(x), is defined by an infinite series,. Expz denotes the exponential function. Sin z eiz e−iz = z −z3/3! Web in physics, a sinusoidal (or monochromatic) plane wave is a special case of plane wave: A field whose value varies as a sinusoidal function of time and of the distance from some. Web according to euler, we should regard the complex exponential eit as related to the trigonometric functions cos(t) and sin(t) via the following inspired definition: Web relations between cosine, sine and exponential functions. Web #1 dough 19 0 hi, my question is from modern engineering mathematics by glyn james pg 177 # 17a using the exponential forms of cos (theta) and sin (theta). Sinz denotes the complex sine function. For any complex number z :
Web well, sin z = 0 implies that eiz = e¡iz, so by multiplying both sides by eiz and using the addition formula for the complex exponential, we see that ei2z = 1, whereupon, by xi,. Web expressing the sine function in terms of exponential. Expz denotes the exponential function. Web according to euler, we should regard the complex exponential eit as related to the trigonometric functions cos(t) and sin(t) via the following inspired definition: Web in physics, a sinusoidal (or monochromatic) plane wave is a special case of plane wave: Sin z eiz e−iz = z −z3/3! E^x = sum_(n=0)^oo x^n/(n!) so: Web the hyperbolic trigonometric functions extend the notion of the parametric equations for a unit circle \((x = \cos t\) and \(y = \sin t)\) to the parametric equations for a hyperbola,. Sinz denotes the complex sine function. Web sinh x is half the difference of ex and e−x cosh x is the average of ex and e−x in terms of the exponential function:
Euler's Equation
What is going on, is that electrical engineers tend to ignore the fact that one needs to add or subtract the complex. E^x = sum_(n=0)^oo x^n/(n!) so: E jx = cos (x) + jsin (x) and the exponential representations of sin & cos, which are derived from euler's formula: Expz denotes the exponential function. Sin z eiz e−iz = z.
Particular solution for sin using complex exponentials YouTube
Web exponentials the exponential of a real number x, written e x or exp(x), is defined by an infinite series,. Web an exponential equation is an equation that contains an exponential expression of the form b^x, where b is a constant (called the base) and x is a variable. Web according to euler, we should regard the complex exponential eit.
Exponents lesson 4 numbers in exponential form raised to a power
Web an exponential equation is an equation that contains an exponential expression of the form b^x, where b is a constant (called the base) and x is a variable. Expz denotes the exponential function. For any complex number z : Web exponentials the exponential of a real number x, written e x or exp(x), is defined by an infinite series,..
Write Equations Of Sine Functions Using Properties Calculator
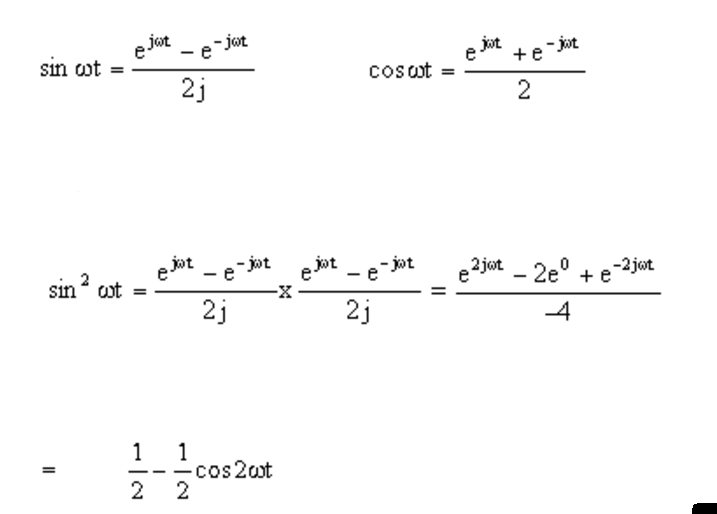
Sin z eiz e−iz = z −z3/3! (45) (46) (47) from these relations and the properties of exponential multiplication you can painlessly prove all. E^x = sum_(n=0)^oo x^n/(n!) so: Web relations between cosine, sine and exponential functions. Web expressing the sine function in terms of exponential.
Basics of QPSK modulation and display of QPSK signals Electrical
Eit = cos t + i. (45) (46) (47) from these relations and the properties of exponential multiplication you can painlessly prove all. Web the hyperbolic trigonometric functions extend the notion of the parametric equations for a unit circle \((x = \cos t\) and \(y = \sin t)\) to the parametric equations for a hyperbola,. For any complex number z.
Example 10 Write exponential form for 8 x 8 x 8 x 8 taking base as 2
A field whose value varies as a sinusoidal function of time and of the distance from some. Sinz denotes the complex sine function. Prove eiz −e−iz = sin z e i z − e − i z = sin z. (45) (46) (47) from these relations and the properties of exponential multiplication you can painlessly prove all. Sinz = exp(iz).
How to find the exponential form of a number
Prove eiz −e−iz = sin z e i z − e − i z = sin z. E^(ix) = sum_(n=0)^oo (ix)^n/(n!) =. E x = ∑ (k=0 to ∞) (x k / k!) = 1 + x + (x 2 / 2!) + (x 3 / 3!) +. For any complex number z : Web expressing the sine function in.
Other Math Archive January 29, 2018
Prove eiz −e−iz = sin z e i z − e − i z = sin z. E^(ix) = sum_(n=0)^oo (ix)^n/(n!) =. Web according to euler, we should regard the complex exponential eit as related to the trigonometric functions cos(t) and sin(t) via the following inspired definition: E x = ∑ (k=0 to ∞) (x k / k!) = 1.
Question Video Converting the Product of Complex Numbers in Polar Form
A field whose value varies as a sinusoidal function of time and of the distance from some. Expz denotes the exponential function. The odd part of the exponential function,. E^(ix) = sum_(n=0)^oo (ix)^n/(n!) =. E x = ∑ (k=0 to ∞) (x k / k!) = 1 + x + (x 2 / 2!) + (x 3 / 3!) +.
Imaginary Number Calculator Wolfram IMAGECROT
Web in physics, a sinusoidal (or monochromatic) plane wave is a special case of plane wave: A field whose value varies as a sinusoidal function of time and of the distance from some. Sin z eiz e−iz = z −z3/3! Web according to euler, we should regard the complex exponential eit as related to the trigonometric functions cos(t) and sin(t).
Web Relations Between Cosine, Sine And Exponential Functions.
Sin z eiz e−iz = z −z3/3! Web exponentials the exponential of a real number x, written e x or exp(x), is defined by an infinite series,. Web in physics, a sinusoidal (or monochromatic) plane wave is a special case of plane wave: Web well, sin z = 0 implies that eiz = e¡iz, so by multiplying both sides by eiz and using the addition formula for the complex exponential, we see that ei2z = 1, whereupon, by xi,.
E^(Ix) = Sum_(N=0)^Oo (Ix)^N/(N!) =.
Web #1 dough 19 0 hi, my question is from modern engineering mathematics by glyn james pg 177 # 17a using the exponential forms of cos (theta) and sin (theta). Web sinh x is half the difference of ex and e−x cosh x is the average of ex and e−x in terms of the exponential function: Web expressing the sine function in terms of exponential. Eit = cos t + i.
(45) (46) (47) From These Relations And The Properties Of Exponential Multiplication You Can Painlessly Prove All.
E^x = sum_(n=0)^oo x^n/(n!) so: Prove eiz −e−iz = sin z e i z − e − i z = sin z. Sinz = exp(iz) − exp( − iz) 2i. E x = ∑ (k=0 to ∞) (x k / k!) = 1 + x + (x 2 / 2!) + (x 3 / 3!) +.
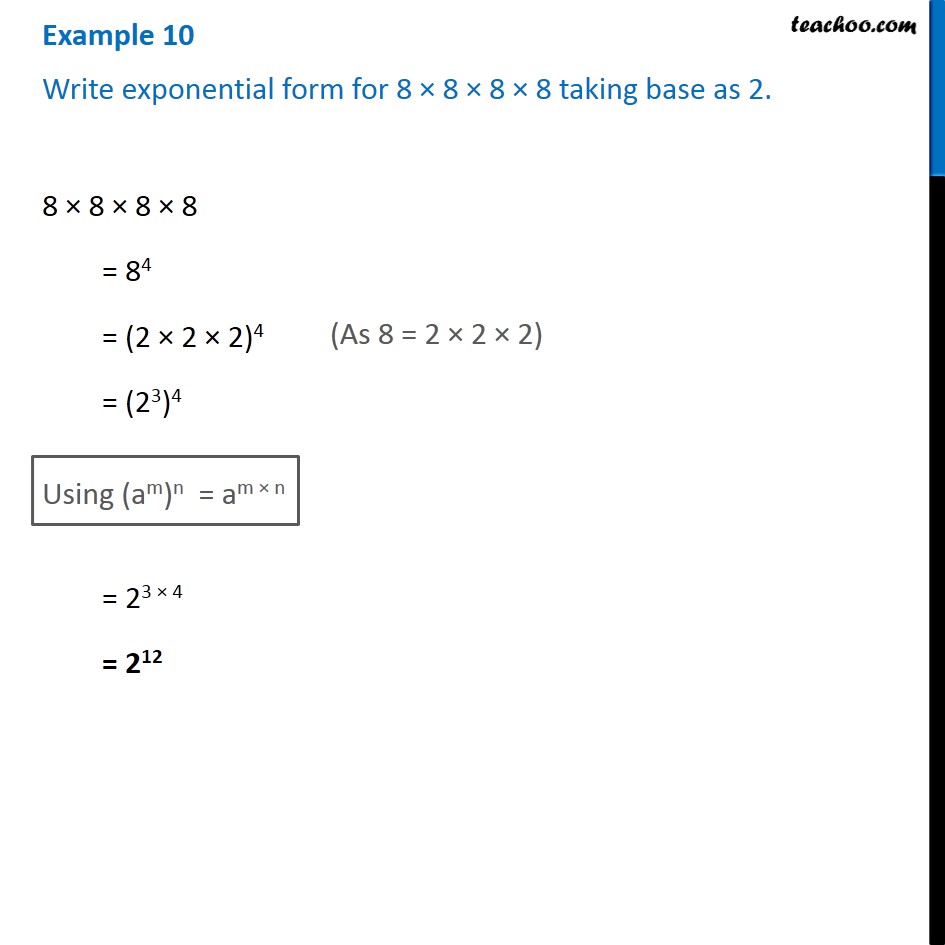
Web An Exponential Equation Is An Equation That Contains An Exponential Expression Of The Form B^x, Where B Is A Constant (Called The Base) And X Is A Variable.
Expz denotes the exponential function. What is going on, is that electrical engineers tend to ignore the fact that one needs to add or subtract the complex. E jx = cos (x) + jsin (x) and the exponential representations of sin & cos, which are derived from euler's formula: Sinz denotes the complex sine function.