General Form Of A Polynomial
General Form Of A Polynomial - It can have any degree. A quadratic function is the polynomial function defined by a quadratic. Web types of polynomial equations linear equations. It is of the form ax + b = 0. F ( x) = a n x n + a n − 1 x n − 1 + a n − 2 x n − 2 +. Web the general form to represent the polynomial is as follows: Polynomials can be added using the associative law of addition (grouping all their terms together into a single sum), possibly followed by reordering (using the commutative law) and combining of like terms. It can have different exponents, where the higher one is called the degree of. (you can also see this on the graph) we. Each expression a i x i a i x i is a term of a.
Web this is called the general form of a polynomial function. A trinomial is a polynomial with 3 terms. A third degree polynomial is called a. Each a i a i is a coefficient and can be any real number, but a n ≠ a n ≠. Write the polynomial in standard form. It can have any degree. Web the three most common polynomials we usually encounter are monomials, binomials, and trinomials. 2x + 3 = 0,. Divide both sides by 2: Web types of polynomial equations linear equations.
It can have any degree. A quadratic function is the polynomial function defined by a quadratic. Web a root is when y is zero: Positive or zero) integer and a a is. (you can also see this on the graph) we. A homogeneous polynomial in two or more variables. Web a homogeneous polynomial in two or more variables. Each a i a i is a coefficient and can be any real number, but a n ≠ a n ≠. Divide both sides by 2: It can have different exponents, where the higher one is called the degree of.
General form of a Polynomial/part 2/class 10/Polynomial/ncert
It can have different exponents, where the higher one is called the degree of. Web yes, if α ∈ f α ∈ f, then by f(α) f ( α) we just mean the polynomial obtained by replacing each occurence of x x by α α. Web the general form to represent the polynomial is as follows: + a 1 x.
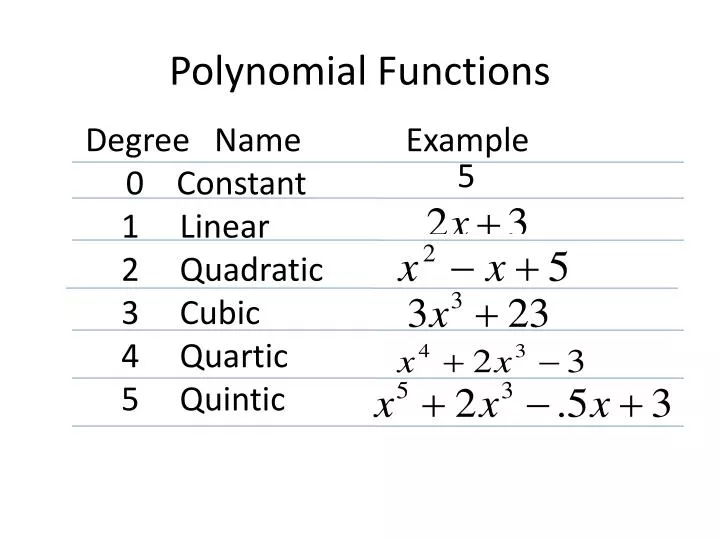
Polynomial functions
Web the equations formed with variables, exponents and coefficients are called as polynomial equations. Web a polynomial of degree n is a function of the form f(x) = a nxn +a n−1xn−1 +.+a2x2 +a1x+a0 where the a’s are real numbers (sometimes called the coefficients of the. For example, if and then the sum A trinomial is a polynomial with 3.
nth Degree Polynomial General form Concept & Solved Examples Cuemath
Polynomials can be added using the associative law of addition (grouping all their terms together into a single sum), possibly followed by reordering (using the commutative law) and combining of like terms. These are the polynomial equations with degree 1. Web the general form to represent the polynomial is as follows: Web in mathematics, a quadratic polynomial is a polynomial.
Polynomial Functions Types Graph Solved Examples Cuemath
Web the general form of a polynomial function with degree n is: + a 1 x + a 0 here, a 0 ,….a n is a constant x is a variable types of. Web in mathematics, a quadratic polynomial is a polynomial of degree two in one or more variables. And that is the solution: Web this is called the.
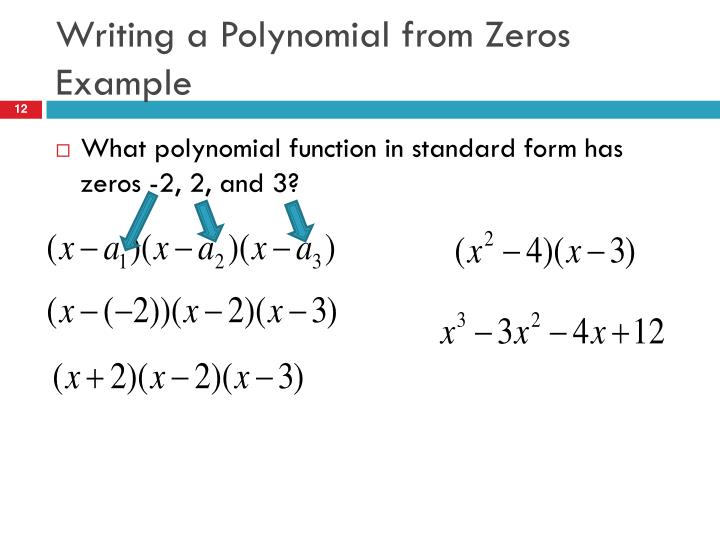
PPT Polynomials, Linear Factors, Zeros PowerPoint Presentation ID
Web steps for the subtraction of polynomials. Positive or zero) integer and a a is. Web a homogeneous polynomial in two or more variables. Write the polynomial in standard form. Web a root is when y is zero:
Polynomial functions
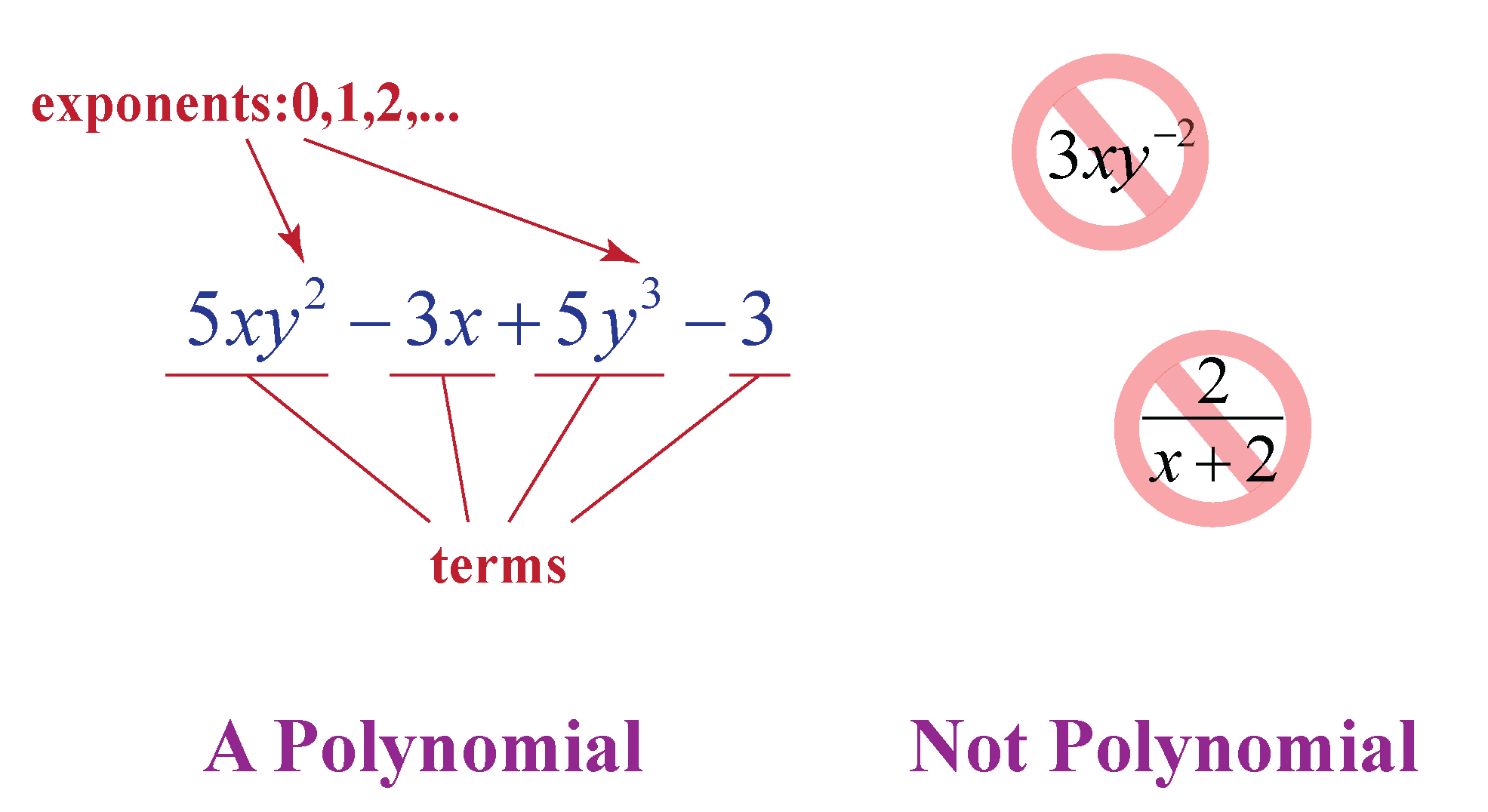
Each expression a i x i a i x i is a term of a. Monomials are polynomials that contain only one term. Write the polynomials vertically (one below the other) such that terms are. It is of the form ax + b = 0. Subtract 1 from both sides:
PPT Polynomial Functions PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID
Web yes, if α ∈ f α ∈ f, then by f(α) f ( α) we just mean the polynomial obtained by replacing each occurence of x x by α α. It can have different exponents, where the higher one is called the degree of. A trinomial is a polynomial with 3 terms. Web the general form to represent the.
nth Degree Polynomial General form Concept & Solved Examples Cuemath
It can have different exponents, where the higher one is called the degree of. And that is the solution: These are the polynomial equations with degree 1. Polynomials can be added using the associative law of addition (grouping all their terms together into a single sum), possibly followed by reordering (using the commutative law) and combining of like terms. Positive.
3.3.i Writing a Polynomial in General Form YouTube
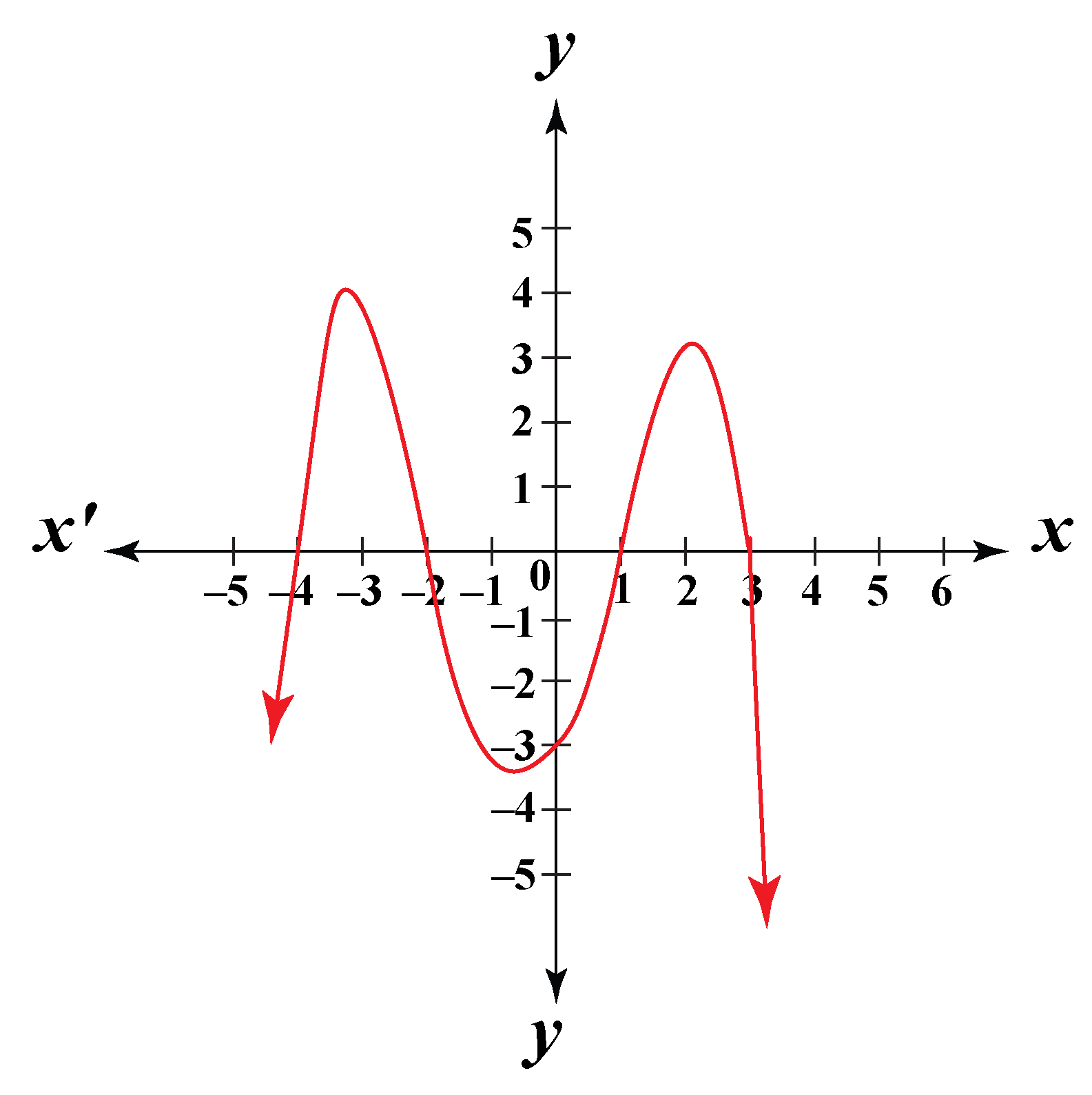
Web a root is when y is zero: Each expression a i x i a i x i is a term of a. And that is the solution: Web types of polynomial equations linear equations. Positive or zero) integer and a a is.
nth Degree Polynomial General form Concept & Solved Examples Cuemath
Polynomials can be added using the associative law of addition (grouping all their terms together into a single sum), possibly followed by reordering (using the commutative law) and combining of like terms. Each expression a i x i a i x i is a term of a. Monomials are polynomials that contain only one term. It can have different exponents,.
Divide Both Sides By 2:
A homogeneous polynomial in two or more variables. Each a i a i is a coefficient and can be any real number, but a n ≠ a n ≠. Web the general form to represent the polynomial is as follows: Write the polynomials vertically (one below the other) such that terms are.
It Is Of The Form Ax + B = 0.
2x + 3 = 0,. Web yes, if α ∈ f α ∈ f, then by f(α) f ( α) we just mean the polynomial obtained by replacing each occurence of x x by α α. Positive or zero) integer and a a is. (you can also see this on the graph) we.
+ A 1 X + A 0 Here, A 0 ,….A N Is A Constant X Is A Variable Types Of.
Write the polynomial in standard form. A quadratic function is the polynomial function defined by a quadratic. A trinomial is a polynomial with 3 terms. For example, if and then the sum
Web First Note, A Trinomial Is Not Necessarily A Third Degree Polynomial.
Subtract 1 from both sides: Polynomials can be added using the associative law of addition (grouping all their terms together into a single sum), possibly followed by reordering (using the commutative law) and combining of like terms. Web to prove the roots of the linear polynomial formula, let us consider the general form of a linear polynomial p (x) = ax + b, where a and b are real numbers with a ≠ 0. Web a root is when y is zero: