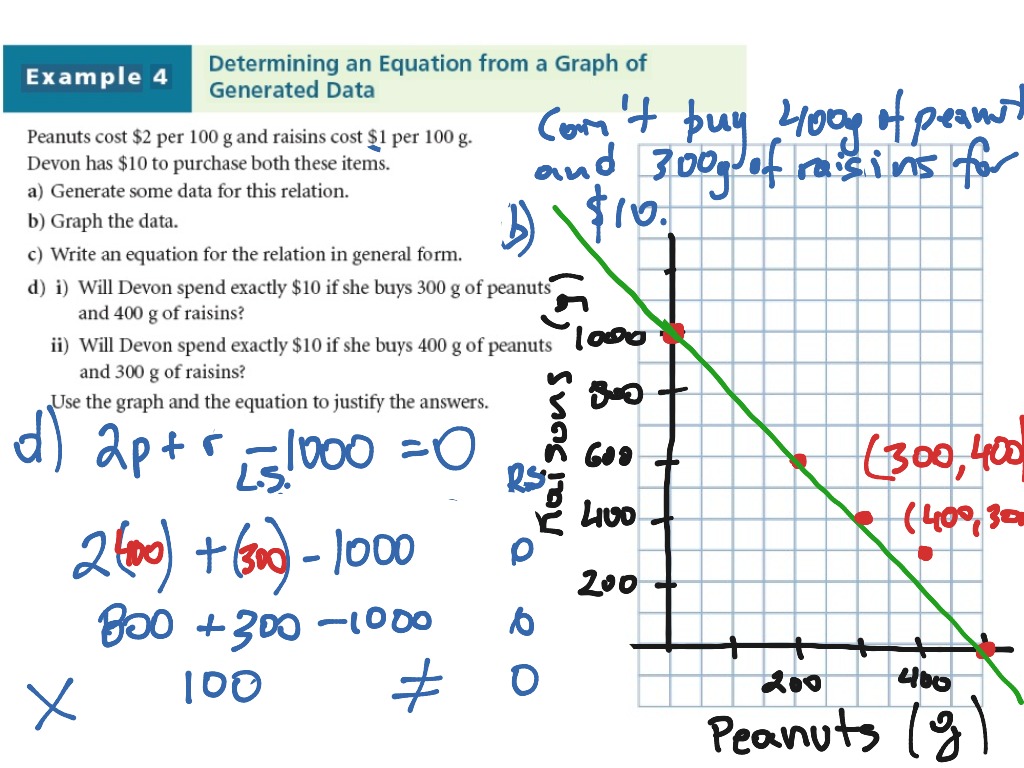
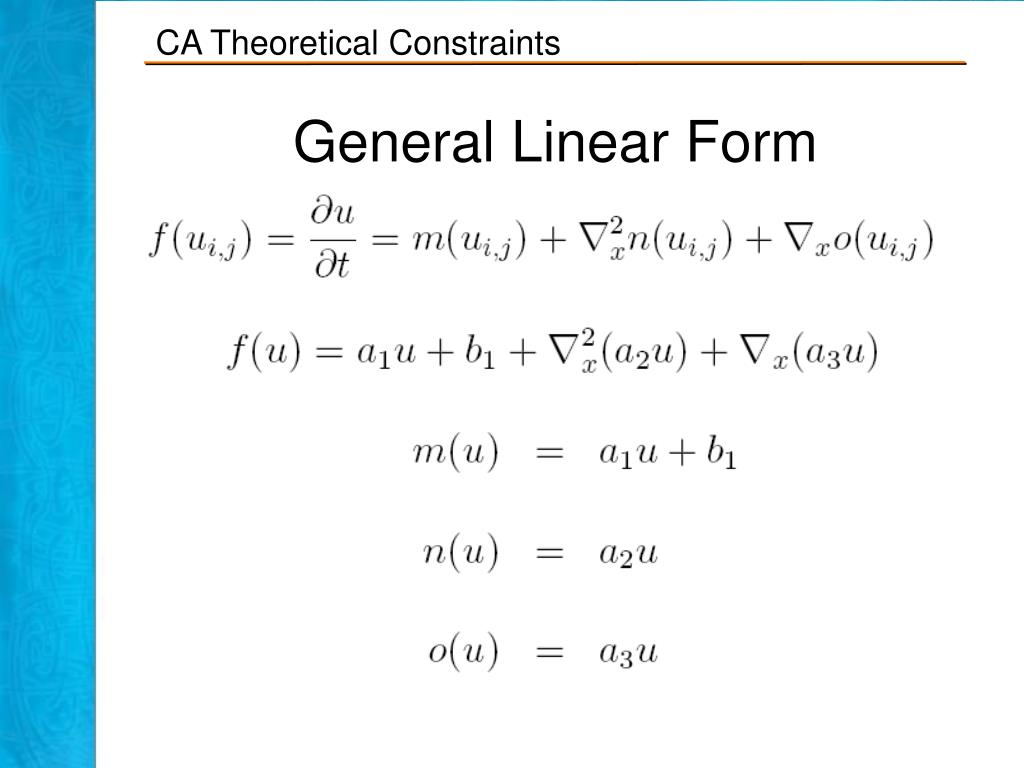
General Linear Form
General Linear Form - From the slope, calculate variables a and b with this equation. Web in general, the behavior of a linear system is determined by the relationship between the number of equations and the number of unknowns. The set of all real matrices forms a real lie subgroup. The general form ax+by+c=0 is one of the many different forms you can write linear functions in. And there is also the general form of the equation of a straight line: Thus, to convert to general linear form, first isolate x and y on one side and. Web a linear form on a vector space $v$ is an element of $v^*$. Web the general form of the equation of a straight line is 𝑎 𝑥 + 𝑏 𝑦 + 𝑐 = 0, where 𝑎, 𝑏, and 𝑐 are constants. Ax + by + c = 0 (a and b cannot both be 0) example: Web the term general linear model (glm) usually refers to conventional linear regression models for a continuous response variable given continuous and/or categorical predictors.
From the slope, calculate variables a and b with this equation. Then reduce the resulting fraction to. Thus, to convert to general linear form, first isolate x and y on one side and. Web there are three main forms of linear equations. Web there are many ways of writing linear equations, but they usually have constants (like 2 or c) and must have simple variables (like x or y). It is for students from year 9 who are preparing for gcse. For example, 2x+3y=5 is a linear equation in standard form. 7x + 5 = 0. This equation is called the general form for a line. It has the following general structure.
Ax + by + c = 0 (a and b cannot both be 0) example: 7x + 5 = 0. This is a ks3 lesson on a linear equations in general form. Web there are three main forms of linear equations. Web the term general linear model (glm) usually refers to conventional linear regression models for a continuous response variable given continuous and/or categorical predictors. Web this equation is often also written as: Here, \maroonc {m} m and \greene {b} b can be any two real numbers. By selecting various values for a and b, this form can represent any linear equation in one variable after such an equation has been simpli represents the numerical equation. Y − y 1 = m ( x − x 1) Ax + by + c = 0 general form of a line.
Solved What is the form of the general linear model? The
Web the general form of the equation of a straight line is: The set of all real matrices forms a real lie subgroup. Standard form of a line. The general form ax+by+c=0 is one of the many different forms you can write linear functions in. Web in general, the behavior of a linear system is determined by the relationship between.
PPT 1.2 Linear Equations in Two Variables PowerPoint Presentation
Web what is the general form linear equation? Web the general form of the equation of a straight line is 𝑎 𝑥 + 𝑏 𝑦 + 𝑐 = 0, where 𝑎, 𝑏, and 𝑐 are constants. Web the term general linear model (glm) usually refers to conventional linear regression models for a continuous response variable given continuous and/or categorical predictors..
Linear Equations Definition, Formula, Examples & Solutions
Standard form of a line. The graph of this equation is a straight line. Ax + by + c = 0. 7x + 5 = 0. It includes multiple linear regression, as well as anova and ancova (with fixed effects only).
MathCamp321 Algebra 2 Linear Equations in General Form YouTube
And there is also the general form of the equation of a straight line: Two of the forms require slope, so let's find that first. It includes multiple linear regression, as well as anova and ancova (with fixed effects only). Ax + by + c = 0 general form of a line. These correspond to the inclusions gl(n, r) <.
The General Form of a Linear Equation ax+by+c=0 YouTube
Web the general linear group over the field of complex numbers, gl(n, c), is a complex lie group of complex dimension n 2. Ax + by + c = 0 (a and b cannot both be 0) example: Web there are three main forms of linear equations. The set of all real matrices forms a real lie subgroup. It includes.
The General Form of a Linear Equation YouTube
Thus, to convert to general linear form, first isolate x and y on one side and. The general form ax+by+c=0 is one of the many different forms you can write linear functions in. Standard form of a line. Y − y 1 = m ( x − x 1) Ax + b = 0.
General Form Of A Linear Equation Tessshebaylo
For example, 2x+3y=5 is a linear equation in standard form. Web the goal in converting an equation to general linear form is to place x and y on one side of the equation and convert all coefficients (and the constant term) to integers. Calculate the variable c by applying one. All straight lines can be represented by an equation in.
General Form of Linear Equations Math, Linear Equations ShowMe
Web there are many ways of writing linear equations, but they usually have constants (like 2 or c) and must have simple variables (like x or y). It includes multiple linear regression, as well as anova and ancova (with fixed effects only). The general form is not always the most useful form, and you may prefer to use: Web the.
PPT Simulating Spatial Partial Differential Equations with Cellular
7x + 5 = 0. Here, in general means that a different behavior may occur for specific values of the coefficients of the equations. The general form is not always the most useful form, and you may prefer to use: Ax + by = c. Ax + by + c = 0 general form of a line.
Introduction to General (Standard) Form of a Linear Equation (L11.4A
From the slope, calculate variables a and b with this equation. It includes multiple linear regression, as well as anova and ancova (with fixed effects only). Thus, to convert to general linear form, first isolate x and y on one side and. This equation is called the general form for a line. Ax + by + c = 0 general.
These Correspond To The Inclusions Gl(N, R) < Gl(N, C) < Gl(2N, R),
This form is also very useful when solving systems of two linear equations. Web the standard form for linear equations in two variables is ax+by=c. All straight lines can be represented by an equation in general form. Two of the forms require slope, so let's find that first.
Calculate The Variable C By Applying One.
It includes multiple linear regression, as well as anova and ancova (with fixed effects only). Here, \maroonc {m} m and \greene {b} b can be any two real numbers. Ax + by + c = 0 general form of a line. Web therefore, the general form of a linear equation in one variable is.
3X + 2Y − 4 = 0.
Web the term general linear model (glm) usually refers to conventional linear regression models for a continuous response variable given continuous and/or categorical predictors. You would plug in 0 for x. The coefficients may be considered as parameters of the equation, and may be arbitrary expressions, provided they do not contain any of the variables. Web the general form of the equation of a straight line is:
Web A Linear Form On A Vector Space $V$ Is An Element Of $V^*$.
The set of all real matrices forms a real lie subgroup. Y − y 1 = m ( x − x 1) Ax + by + c = 0 (a and b cannot both be 0) example: Web there are three main forms of linear equations.