In Which Geologic Period Did The Wave Form
In Which Geologic Period Did The Wave Form - The rate at which the temperature in the air decreases with altitude is known as the _____ rate. Web over 41 million acres are connected through the waters that flow to and through chesapeake bay. An example of physical weathering is. Web at the wave, swirling sandstone of different colors create nature’s art. 36°58′04″n 112°00′41″w the magic crest of south coyote buttes. Determining the distance along the earth's surface from a seismic station to the epicenter of an earthquake is based on the difference in arrival times between. Web november 2, 2012 the wave, a sandstone formation in northern arizona. First, the materials were deposited. Web what is the name of the supercontinent that broke up to form the modern geography as a result of continental drift? Inspiring stewardship across this vast region supports recreation, business, tourism, learning, and a thriving natural.
Which two key geologic phenomena are associated with the process of subduction? Web it is interesting to note that natural catastrophes devastated the world just as each geologic era ended and another era began to form on earth. A thunderstorm cloud that reaches to the tropopause and spreads into a flat sheet is called a (n) anvil cloud. An example of physical weathering is. Web the short answer: Water in underground sediment or rock is referred to as. Although it is in an isolated area, there is a continual drove of travellers through the town to view the rock. Its odd shape comes from two main processes: Web this time period took place 359 to 299 million years ago. The layers and patterns also reveal the story of the geological history of the region.
As its name suggests, wave rock (figure 1) resembles an enormous. Web november 2, 2012 the wave, a sandstone formation in northern arizona. B) the gravitational force of earth was not strong enough to hold them. A magma with a high silica content is called. One of these planetesimals developed into earth. Along with these catastrophic changes, after which appeared new species, existing species were almost always wiped out. The first p wave and the first s wave. A) these gases were burned off by solar radiation. The layers and patterns also reveal the story of the geological history of the region. D) acid rain removed these gases from the atmosphere.
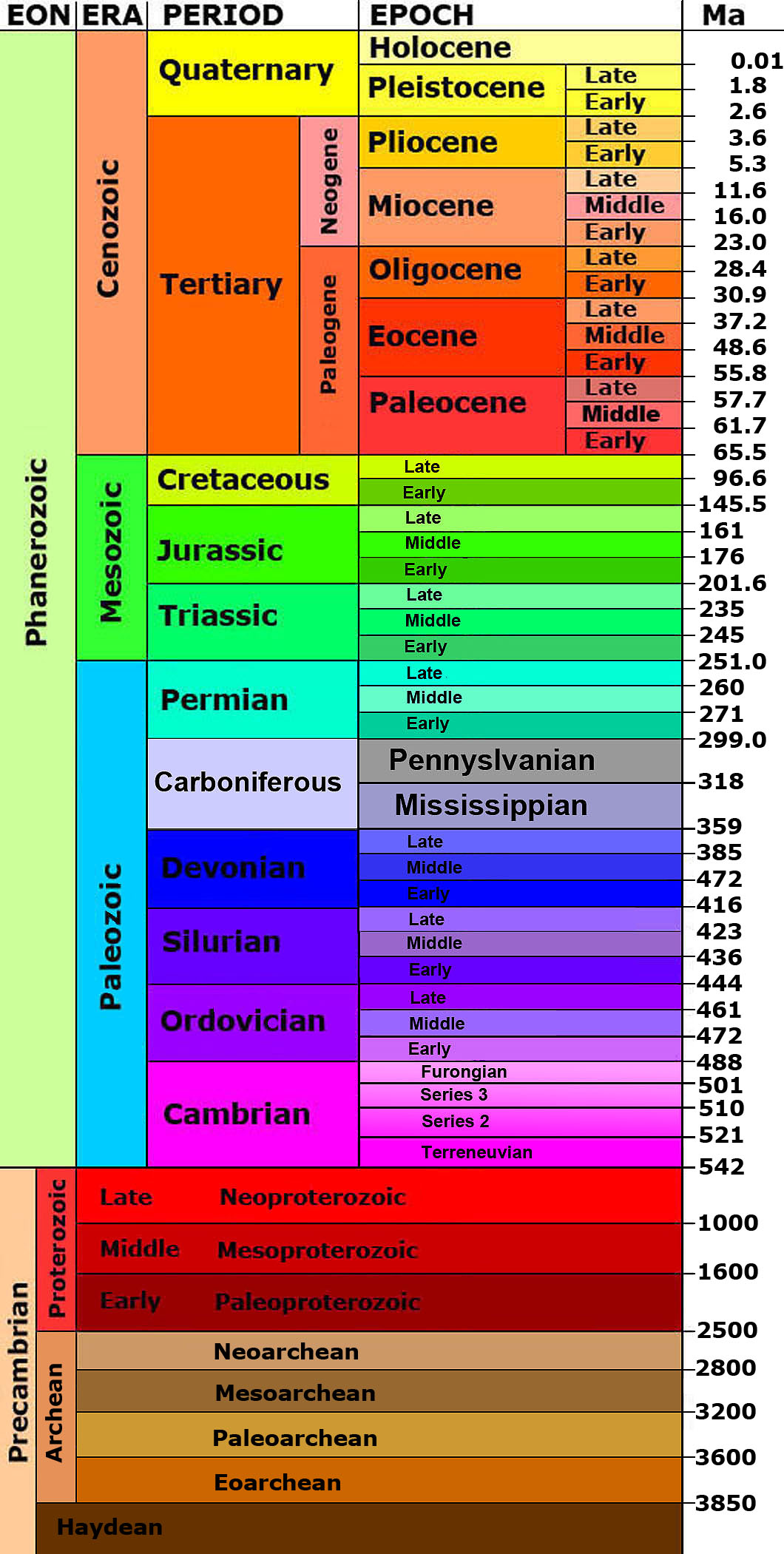
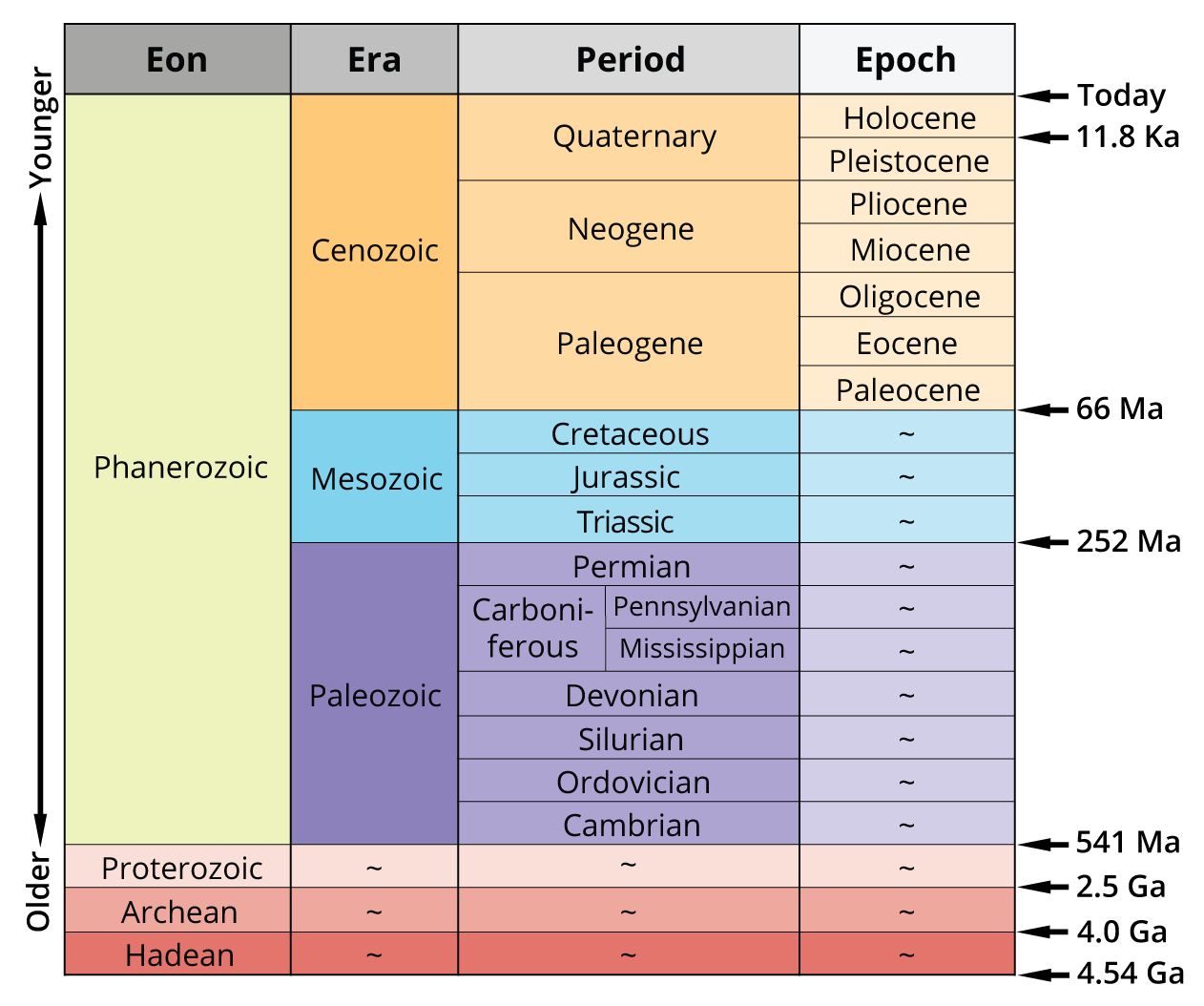
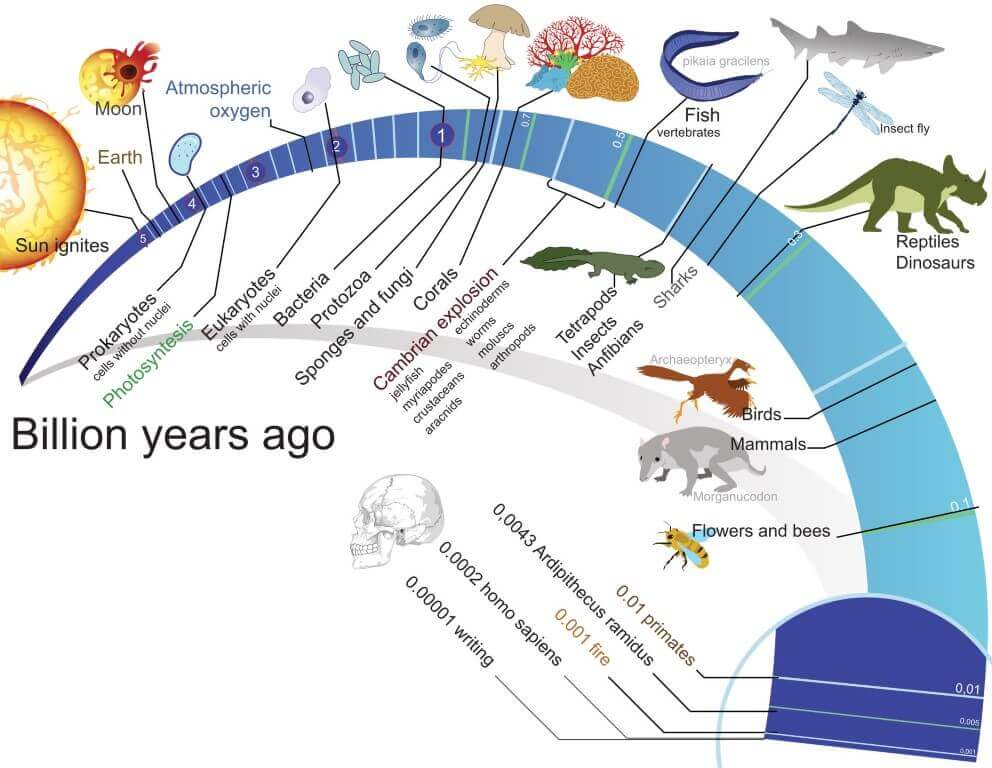
Geologic Time Scale
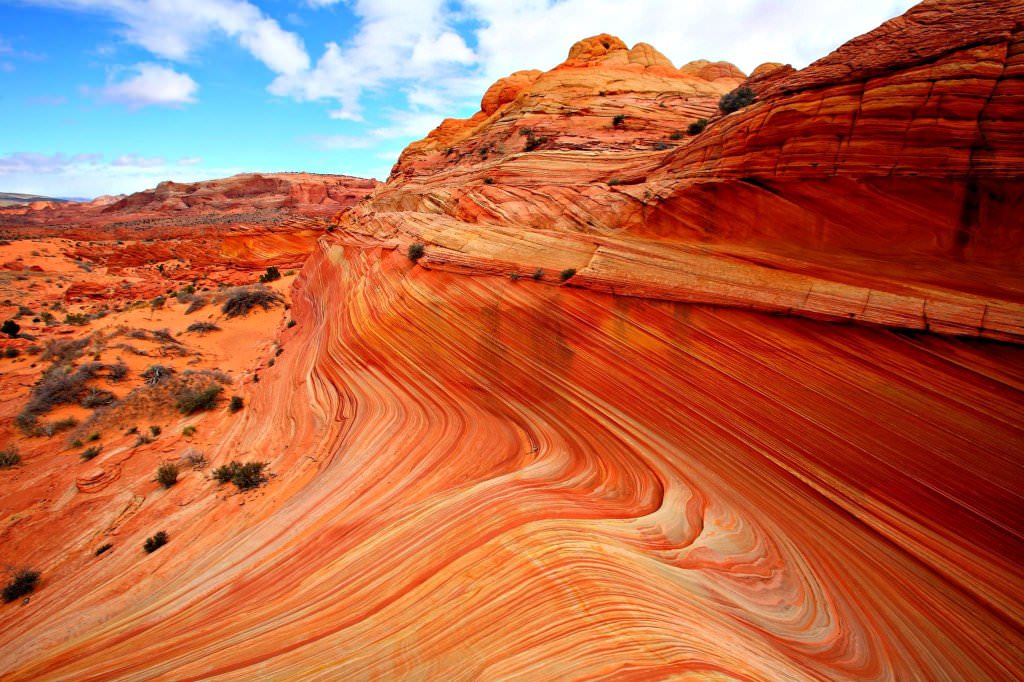
The wave is a sandstone rock formation located in arizona, us, near its northern border with utah. Although it is in an isolated area, there is a continual drove of travellers through the town to view the rock. Web over 41 million acres are connected through the waters that flow to and through chesapeake bay. Volcanoes and underground (batholiths, sills,.
Geology in Motion Wave Rock, Australia An unusual geologic feature
Web what is the name of the supercontinent that broke up to form the modern geography as a result of continental drift? Web these models place earth’s age at approximately 4.5 billion years old. The carboniferous period, part of the late paleozoic era, takes its name from large underground coal deposits that date to it. Web james hutton is considered.
Climate Change And The Astrobiology Of The Anthropocene New Hampshire
Web james hutton is considered the father of modern geology because he recognized that geologic processes take place very slowly over long periods of time. The rate at which the temperature in the air decreases with altitude is known as the _____ rate. One of these planetesimals developed into earth. The melting associated with the addition of volatiles to rocks.
GEOLOGICTIMESCALECOURTESYGSA Protomythological Forms
Web november 2, 2012 the wave, a sandstone formation in northern arizona. Along with these catastrophic changes, after which appeared new species, existing species were almost always wiped out. The layers and patterns also reveal the story of the geological history of the region. In which geologic period did the wave form? To locate the epicenter of an earthquake, it.
The Wave Series 'Most mysterious geological formations'
Web 8) why is there virtually no hydrogen and helium present in the atmosphere today? The melting associated with the addition of volatiles to rocks is referred to as. 36°58′04″n 112°00′41″w the magic crest of south coyote buttes. As its name suggests, wave rock (figure 1) resembles an enormous. Web hyden rock began forming during the cretaceous period over 100.
Best Geological Formation Winners (2016) USA TODAY 10Best
Which two key geologic phenomena are associated with the process of subduction? First, the materials were deposited. Sounds like a good choice. Determining the distance along the earth's surface from a seismic station to the epicenter of an earthquake is based on the difference in arrival times between. Water in underground sediment or rock is referred to as.
ere geologiche laCOOLtura
Which one of these is not a challenge for hikers in the wave? Along with these catastrophic changes, after which appeared new species, existing species were almost always wiped out. Web 8) why is there virtually no hydrogen and helium present in the atmosphere today? What did ancient people think fossils were? Web during the hadean period the late heavy.
Chart of Geological Time (Infographic)
Web over 41 million acres are connected through the waters that flow to and through chesapeake bay. Water in underground sediment or rock is referred to as. Inspiring stewardship across this vast region supports recreation, business, tourism, learning, and a thriving natural. D) acid rain removed these gases from the atmosphere. Web these models place earth’s age at approximately 4.5.
Geological Timeline (With images) Geologic time scale, History of
A) these gases were burned off by solar radiation. What did ancient people think fossils were? Web november 2, 2012 the wave, a sandstone formation in northern arizona. Sounds like a good choice. Place letters on the lines along the right side of the cross section to indicate the relative ages of the rock units and other features (unconformities, faut.
Geological Time Scale Hadean, Archean, Proterozoic & Phanerozoic PMF IAS
Web this time period took place 359 to 299 million years ago. Web even after those first scorching millennia, however, the planet has often been much warmer than it is now. The first p wave and the first s wave. Which one of these is not a challenge for hikers in the wave? The place is at the southwestern margin.
36°58′04″N 112°00′41″W The Magic Crest Of South Coyote Buttes.
Web during the hadean period the late heavy bombardment occurred (approximately 3800 to 4100 ma) during which a large number of impact craters are believed to have formed on the moon, and by inference on earth, mercury, venus, and mars as well. Which two key geologic phenomena are associated with the process of subduction? Place letters on the lines along the right side of the cross section to indicate the relative ages of the rock units and other features (unconformities, faut from oldest (first) to youngest (ast) cambrian pracambrian parow oping mar limestone bright angel shak. Web hyden rock began forming during the cretaceous period over 100 million years ago when australia broke away from antarctica.
Sounds Like A Good Choice.
Web tons of oxygen and tough trees, giant insects and amphibians flying and crawling all over the damn place? D) acid rain removed these gases from the atmosphere. The rate at which the temperature in the air decreases with altitude is known as the _____ rate. The long answer, and the much more interesting one, begins nearly 200 million years ago.
In Which Geologic Period Did The Wave Form?
One of the warmest times was during the geologic period known as the neoproterozoic, between 600 and 800 million years ago. Web at the wave, swirling sandstone of different colors create nature’s art. Web 8) why is there virtually no hydrogen and helium present in the atmosphere today? Geologists classify wave rock as a flared slope, a concave bedrock surface at the base of the inselberg.
Particles In The Solar Nebula Condensed To Form Solid Grains, And With Increasing Electrostatic And Gravitational Influences They Eventually Clumped Together Into Fragments Or Chunks Of Rock.
Volcanoes and underground (batholiths, sills, dikes) sedimentary rocks. As its name suggests, wave rock (figure 1) resembles an enormous. Water in underground sediment or rock is referred to as. The melting associated with the addition of volatiles to rocks is referred to as.