Ionic Bonds Form Between Atoms With Complementary
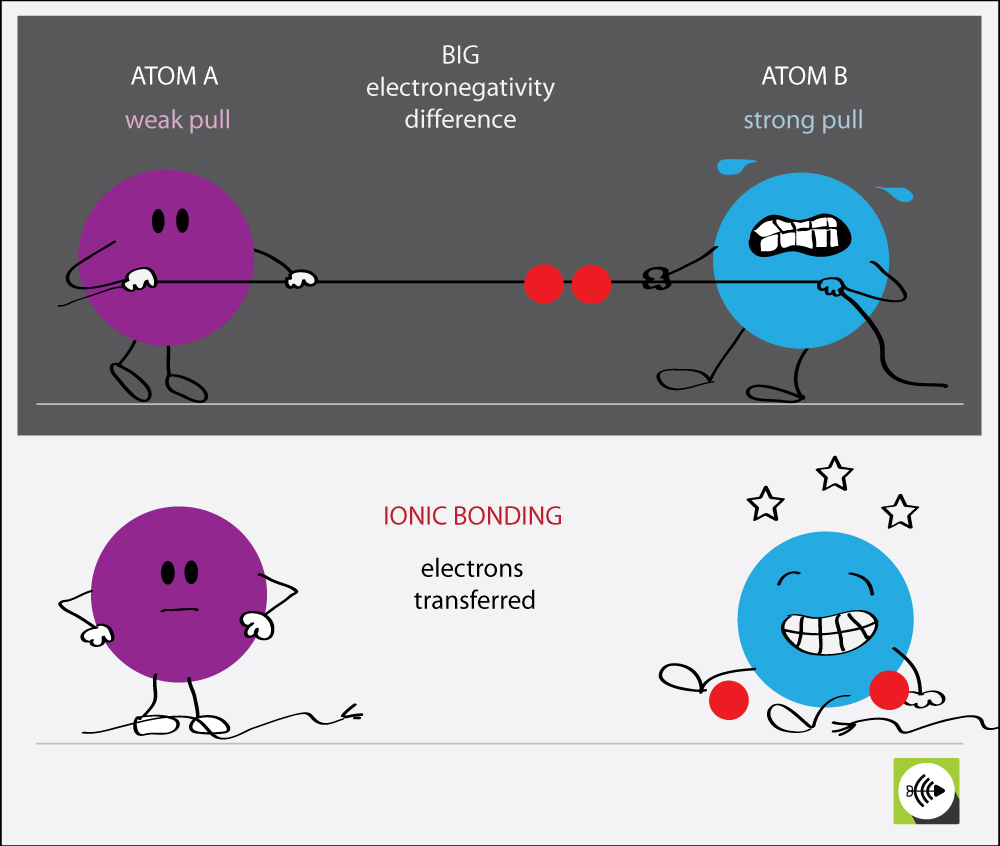
Ionic Bonds Form Between Atoms With Complementary - Ionic bonds form between two or more atoms by the transfer of one or more electrons between atoms. In contrast, atoms with the same electronegativity share electrons in covalent bonds, because neither atom preferentially attracts or repels the shared electrons. For example, sodium cations (positively charged ions) and chlorine anions (negatively charged ions) are connected via ionic bonds in sodium chloride, or table. These ions then attract each other electrostatically to form a stable crystalline lattice. These ions attract each other. One type of chemical bond is an ionic bond. Web types of chemical bonds including covalent, ionic, and hydrogen bonds and london dispersion forces. Ionic bonds result from the attraction between oppositely charged ions. Ionic bonds require at least one electron donor and one electron acceptor. In covalent compounds, atoms form covalent bonds that consist of electron pairs shared between two adjacent atomic nuclei.
Ions are created when an atom loses or gains an electron. Ionic bonds require at least one electron donor and one electron acceptor. Web ionic bond, also called electrovalent bond, type of linkage formed from the electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions in a chemical compound. Web glossary summary glossary introduction learning objectives explain the formation of cations, anions, and ionic compounds predict the charge of common metallic and nonmetallic elements, and write their electron configurations describe the formation of covalent bonds define electronegativity and assess the polarity of covalent bonds In covalent compounds, atoms form covalent bonds that consist of electron pairs shared between two adjacent atomic nuclei. Let’s examine the ionic bond in sodium chloride. Web types of chemical bonds including covalent, ionic, and hydrogen bonds and london dispersion forces. Web atoms interact with each other through the formation of chemical bonds. In contrast, atoms with the same electronegativity share electrons in covalent bonds, because neither atom preferentially attracts or repels the shared electrons. Ionic bonds result from the attraction between oppositely charged ions.
Introduction living things are made up of atoms, but in most cases, those atoms aren’t just floating around individually. Web compounds can be covalent or ionic. In covalent compounds, atoms form covalent bonds that consist of electron pairs shared between two adjacent atomic nuclei. Web atoms interact with each other through the formation of chemical bonds. Let’s examine the ionic bond in sodium chloride. Web ionic bond, also called electrovalent bond, type of linkage formed from the electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions in a chemical compound. Ionic bonds result from the attraction between oppositely charged ions. In ionic bonding, electrons are considered to be transferred completely from one atom to another atom (or group of atoms), forming ions of opposite charge. Ions are created when an atom loses or gains an electron. Such a bond forms when the valence (outermost) electrons of one atom are transferred permanently to another atom.
Chapter 2 Atoms, Molecules and Life Chemistry)
Ionic bonds require at least one electron donor and one electron acceptor. Ionic bonds form between two or more atoms by the transfer of one or more electrons between atoms. Web ionic bond, also called electrovalent bond, type of linkage formed from the electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions in a chemical compound. Web ionic bonding is the complete transfer.
Electronegativity Bond Scale Surfguppy Chemistry made easy for
Ions are created when an atom loses or gains an electron. Web in ionic bonding, atoms transfer electrons to each other. These ions then attract each other electrostatically to form a stable crystalline lattice. Ionic bonds form between two or more atoms by the transfer of one or more electrons between atoms. Instead, they’re usually interacting with other atoms (or.
이온 성 공유 결합과 금속 결합의 차이점 2021 뉴스
In contrast, atoms with the same electronegativity share electrons in covalent bonds, because neither atom preferentially attracts or repels the shared electrons. An example of a covalent compound is ammonia. Web types of chemical bonds including covalent, ionic, and hydrogen bonds and london dispersion forces. Web in ionic bonding, atoms transfer electrons to each other. For example, sodium cations (positively.
Examples of Ionic Bonds and Ionic Compounds
Instead, they’re usually interacting with other atoms (or groups of atoms). An example of a covalent compound is ammonia. Ionic bonds form between two or more atoms by the transfer of one or more electrons between atoms. In contrast, atoms with the same electronegativity share electrons in covalent bonds, because neither atom preferentially attracts or repels the shared electrons. Ionic.
Ionic Bond Definition, Types, Properties & Examples
Ions are created when an atom loses or gains an electron. Web glossary summary glossary introduction learning objectives explain the formation of cations, anions, and ionic compounds predict the charge of common metallic and nonmetallic elements, and write their electron configurations describe the formation of covalent bonds define electronegativity and assess the polarity of covalent bonds Ionic bonds form between.
Chemical Bonds
For example, sodium cations (positively charged ions) and chlorine anions (negatively charged ions) are connected via ionic bonds in sodium chloride, or table. Web glossary summary glossary introduction learning objectives explain the formation of cations, anions, and ionic compounds predict the charge of common metallic and nonmetallic elements, and write their electron configurations describe the formation of covalent bonds define.
Ionic Properties
Web ionic bonding is the complete transfer of valence electron (s) between atoms and is a type of chemical bond that generates two oppositely charged ions. In ionic bonding, electrons are considered to be transferred completely from one atom to another atom (or group of atoms), forming ions of opposite charge. One type of chemical bond is an ionic bond..
Ionic Bonding Presentation Chemistry
In ionic bonding, electrons are considered to be transferred completely from one atom to another atom (or group of atoms), forming ions of opposite charge. Such a bond forms when the valence (outermost) electrons of one atom are transferred permanently to another atom. Ionic bonds require at least one electron donor and one electron acceptor. One type of chemical bond.
Ionic Bond Definition, Types, Properties & Examples
Instead, they’re usually interacting with other atoms (or groups of atoms). In covalent compounds, atoms form covalent bonds that consist of electron pairs shared between two adjacent atomic nuclei. Ionic bonds form between two or more atoms by the transfer of one or more electrons between atoms. In contrast, atoms with the same electronegativity share electrons in covalent bonds, because.
Student Exploration Ionic Bonds Answer Key Quizlet / Ionic Bonds Gizmo
Web in ionic bonding, atoms transfer electrons to each other. Such a bond forms when the valence (outermost) electrons of one atom are transferred permanently to another atom. For example, sodium cations (positively charged ions) and chlorine anions (negatively charged ions) are connected via ionic bonds in sodium chloride, or table. In covalent compounds, atoms form covalent bonds that consist.
Web Atoms Interact With Each Other Through The Formation Of Chemical Bonds.
These ions then attract each other electrostatically to form a stable crystalline lattice. One type of chemical bond is an ionic bond. Instead, they’re usually interacting with other atoms (or groups of atoms). An example of a covalent compound is ammonia.
For Example, Sodium Cations (Positively Charged Ions) And Chlorine Anions (Negatively Charged Ions) Are Connected Via Ionic Bonds In Sodium Chloride, Or Table.
Web types of chemical bonds including covalent, ionic, and hydrogen bonds and london dispersion forces. These ions attract each other. In ionic bonding, electrons are considered to be transferred completely from one atom to another atom (or group of atoms), forming ions of opposite charge. Such a bond forms when the valence (outermost) electrons of one atom are transferred permanently to another atom.
Ionic Bonds Result From The Attraction Between Oppositely Charged Ions.
Let’s examine the ionic bond in sodium chloride. Web compounds can be covalent or ionic. Web in ionic bonding, atoms transfer electrons to each other. In covalent compounds, atoms form covalent bonds that consist of electron pairs shared between two adjacent atomic nuclei.
Ions Are Created When An Atom Loses Or Gains An Electron.
Ionic bonds require at least one electron donor and one electron acceptor. Web glossary summary glossary introduction learning objectives explain the formation of cations, anions, and ionic compounds predict the charge of common metallic and nonmetallic elements, and write their electron configurations describe the formation of covalent bonds define electronegativity and assess the polarity of covalent bonds Introduction living things are made up of atoms, but in most cases, those atoms aren’t just floating around individually. Web ionic bonding is the complete transfer of valence electron (s) between atoms and is a type of chemical bond that generates two oppositely charged ions.


:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/ionic-bond-58fd4ea73df78ca1590682ad.jpg)

.PNG)

.PNG)

