Microeconomics Chapter 20
Microeconomics Chapter 20 - How did john maynard keynes define economics? Web microeconomics the branch of economics that focuses on actions of particular agents within the economy, like households, workers, and business firms model Percentage of people whose income falls below the poverty line. Discrimination in education, hiring, training, and promotions contributes to income inequality. Covers the scope and sequence of most introductory economics courses. Click the card to flip 👆 1. Web causes of income inequality. 20.2 labor productivity and economic growth; Learn how supply and demand determine prices, how companies think about competition, and more! Education and training correlate closely with differences in earnings.
20.5 the tradeoffs of trade policy; Costs that do not change as a result of a decision. Web 20.1 the relatively recent arrival of economic growth; An indirect subsidy from consumers to producers; 20.4 how governments enact trade policy: We hit the traditional topics from a. Web then click on the name of the course: How did john maynard keynes define economics? Web the distributions of income and wealth describe economic inequality the 20 percent of households with the lowest incomes receive about 3 percent of total money income and the 1 percent of households. 20.3 components of economic growth;
How did john maynard keynes define economics? The buying and selling responses of consumers and producers to price changes. Covers the scope and sequence of most introductory economics courses. Percentage of people whose income falls below the poverty line. An absolute level of income set by the federal government for each family size below which a family is deemed to be in poverty. Web causes of income inequality. Transfers to the poor given in the form of goods and services rather than cash. Web microeconomics chapter 20 4.9 (10 reviews) advocates of behavioral economics a. We hit the traditional topics from a. It is much easier to find the start here link, the .
Chapter 12 Imperfect Competition AP Microeconomics Chapter Outlines
An absolute level of income set by the federal government for each family size below which a family is deemed to be in poverty. Web the distributions of income and wealth describe economic inequality the 20 percent of households with the lowest incomes receive about 3 percent of total money income and the 1 percent of households. Learn with flashcards,.
E i
Web what are the three main goals of macroeconomics? 20.2 international trade and its effects on jobs, wages, and working conditions; In general, the more education, the higher the income. Web microeconomics the branch of economics that focuses on actions of particular agents within the economy, like households, workers, and business firms model Principles of microeconomics, 7th + mindtap economics.
Microeconomics. The costs of production. Chapter 20 online presentation
20.2 labor productivity and economic growth; 20.3 components of economic growth; Click the card to flip 👆. Click the card to flip 👆 1. University of california los angeles.
Difference between Microeconomics and Macroeconomics With their Comparisons
It is much easier to find the start here link, the . 20.2 labor productivity and economic growth; Learn how supply and demand determine prices, how companies think about competition, and more! Capital supply and capital markets. An absolute level of income set by the federal government for each family size below which a family is deemed to be in.
【55OFF!】 TRUSCO 板金用切断機 レバーシャP1用部品 NO.14スプリングワッシャー P1014 1個 4507410
Argue that consumers make decisions that. Principles of microeconomics, 7th + mindtap economics printed access card (7th edition) edit edition 86 % (21 ratings) for this chapter’s solutions solutions for chapter 20. Web what are the three main goals of macroeconomics? Web microeconomics the branch of economics that focuses on actions of particular agents within the economy, like households, workers,.
Why do we really want to study Microeconomics ? Economics Tutorials
Web 20.1 the relatively recent arrival of economic growth; (11 of 20 on the chapter homework assignments and 22 of 40 on the chapter. 20.2 labor productivity and economic growth; Covers the scope and sequence of most introductory economics courses. 20.3 arguments in support of restricting imports;
What Is Microeconomics LearningAll
Web then click on the name of the course: Costs that do not change as a result of a decision. The study of the economy as a whole. 20.3 components of economic growth; Capital supply and capital markets.
Microeconomics tutorial chapter 1 ABBE1013 MICROECONOMICS Tutorial 1
20.5 the tradeoffs of trade policy; We hit the traditional topics from a. The study of the economy as a whole. You are then taken to the course's main blackboard page. Transfers to the poor given in the form of goods and services rather than cash.
Chapter 2 Principles of Microeconomics by G Mankiw
Web what are the three main goals of macroeconomics? The buying and selling responses of consumers and producers to price changes. Argue that consumers make decisions that. Web ap econ chapter 20. Ability differences lead to differences in earnings.
A Brief Overview of Microeconomics & Macroeconomics
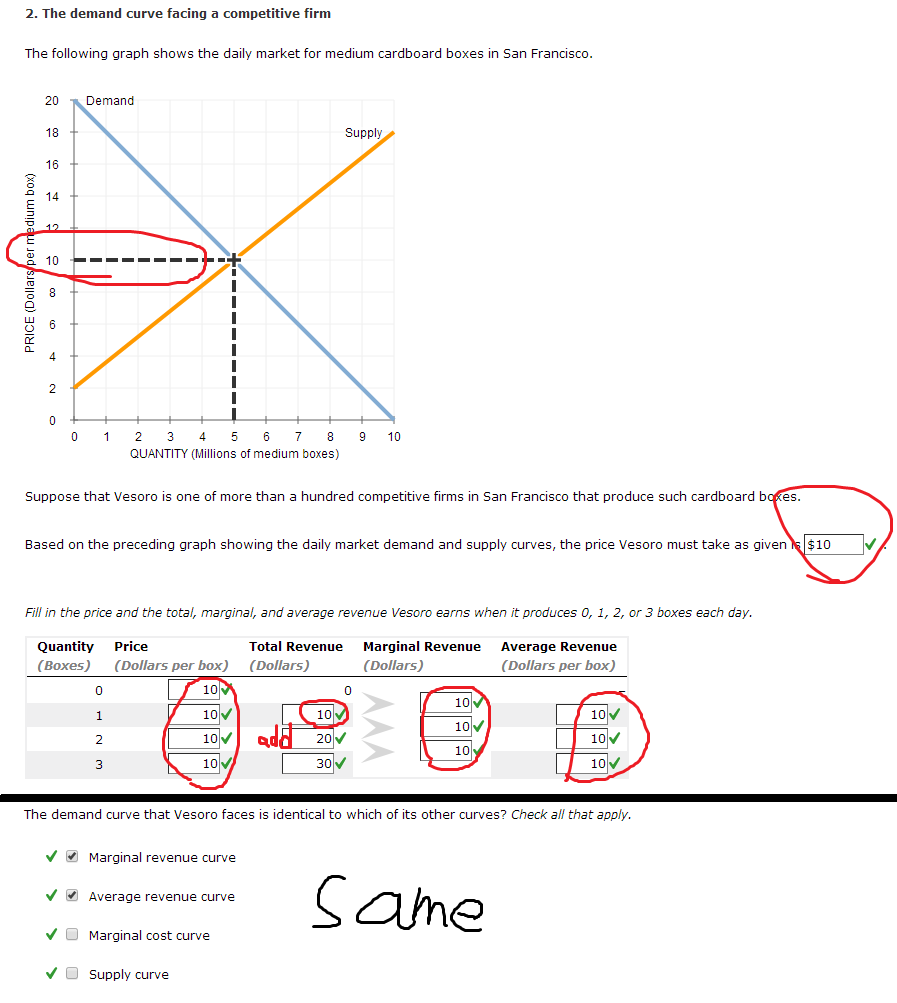
Web microeconomics chapter 20 homework game theory has become more and more important because it click the card to flip 👆 takes into account people's predictably irrational behavior. Web the distributions of income and wealth describe economic inequality the 20 percent of households with the lowest incomes receive about 3 percent of total money income and the 1 percent of.
Education And Training Correlate Closely With Differences In Earnings.
Click the card to flip 👆. Web microeconomics is all about how individual actors make decisions. An indirect subsidy from consumers to producers; Learn with flashcards, games, and more — for free.
Discrimination In Education, Hiring, Training, And Promotions Contributes To Income Inequality.
In general, the more education, the higher the income. 20.4 how governments enact trade policy: The text includes many current examples, which are handled in a politically equitable way. An absolute level of income set by the federal government for each family size below which a family is deemed to be in poverty.
20.3 Arguments In Support Of Restricting Imports;
20.3 components of economic growth; Costs that have already been paid and cannot be recovered. It is much easier to find the start here link, the . Web microeconomics chapter 20 homework game theory has become more and more important because it click the card to flip 👆 takes into account people's predictably irrational behavior.
Covers The Scope And Sequence Of Most Introductory Economics Courses.
Web then click on the name of the course: Transfers to the poor given in the form of goods and services rather than cash. Web 20.1 the relatively recent arrival of economic growth; How did john maynard keynes define economics?