Why Are Halogens And Alkali Metals Likely To Form Ions
Why Are Halogens And Alkali Metals Likely To Form Ions - Why are halogens and alkali metals likely to form ions? Web so halogens tend to gain one electron to form a monovalent anion or negatively charged ion and achieve the stable noble gas configuration. Web reactions of alkali metals with group viia. When they share or transfer electrons. The alkali metals themselves react. Web in the modern iupac nomenclature, this group is known as group (xvii) or group (vii). Web atomic and physical properties of halogens. Web the electrolysis is carried out in an argon atmosphere rather than the nitrogen atmosphere typically used for substances that are highly reactive with o 2 and water because li. Well, the answer lies in the balance show. Web they react aggressively with the halogens to form the alkali metal halides, which are white ionic crystalline compounds that are all soluble in water except lithium fluoride (li f).
Web they react aggressively with the halogens to form the alkali metal halides, which are white ionic crystalline compounds that are all soluble in water except lithium fluoride (li f). Halogen group (group 17) trends. Web halogens need to gain only one electron and alkali metals need to lose one electron in order to reach the nearest noble gas configuration and become more stable. So, as you know, alkaline metals are group one, and they all have. When they share or transfer electrons. Web concept explainers question why are halogens and alkali metals likely to form ions? Less because i’m putting a couple things i know together to get the explanation. However, mercury, the elements of group 13 with oxidation states of 3+, tin (iv),. [4] the word halogen means salt former or salt maker. Web halogens in alkali metals are likely to form ions because their ionization energy is very low because they only need to lose or gain one electron.
Web when do chemical bonds form? Web so halogens tend to gain one electron to form a monovalent anion or negatively charged ion and achieve the stable noble gas configuration. Expert solution step by step solved in 2 steps see solution check. Web when the alkali metals react with the different halogens (group 7 of the periodic table), the group of compounds formed are known as the alkali metals halides. Web atomic and physical properties of halogens. Less because i’m putting a couple things i know together to get the explanation. Web concept explainers question why are halogens and alkali metals likely to form ions? Web okay, so why are hella jin's and alkali metals likely the form ions? They have a low ionization energy, due to them. Web the electrolysis is carried out in an argon atmosphere rather than the nitrogen atmosphere typically used for substances that are highly reactive with o 2 and water because li.
WJEC Chemistry C2 online revision Reactions of alkali metals and halogens
Web ions made from alkaline earth metals, the second group on the periodic table, have a 2+ charge. The halogens are located on the left of the noble gases on the periodic table. Web halogens in alkali metals are likely to form ions because their ionization energy is very low because they only need to lose or gain one electron..
alkali metal Definition, Properties, & Facts Britannica
Web concept explainers question why are halogens and alkali metals likely to form ions? They have a low ionization energy, due to them. Web ions made from alkaline earth metals, the second group on the periodic table, have a 2+ charge. Web halogens need to gain only one electron and alkali metals need to lose one electron in order to.
Solved 141 26. Write down two elements that are members of
Web so halogens tend to gain one electron to form a monovalent anion or negatively charged ion and achieve the stable noble gas configuration. Web when do chemical bonds form? Due to the fact that. So, as you know, alkaline metals are group one, and they all have. Web most common nonmetallic substances such as halogens, halogen acids, sulfur, and.
Why are halogens and alkali metals likely to form ions quizlet? Book Vea
They have a low ionization energy, due to them. Web ions made from alkaline earth metals, the second group on the periodic table, have a 2+ charge. Why are halogens and alkali metals likely to form ions? Web when the alkali metals react with the different halogens (group 7 of the periodic table), the group of compounds formed are known.
Malik Xufyan Only Chemistry Discussion Q. No. 34 why Alkali Metals
Web reactions of alkali metals with group viia. However, mercury, the elements of group 13 with oxidation states of 3+, tin (iv),. So, as you know, alkaline metals are group one, and they all have. When they share or transfer electrons. Web the binary compounds of a metal with the halogens are the halides.
Solved E) All of the halogens have equal strength as
Less because i’m putting a couple things i know together to get the explanation. The halogens are located on the left of the noble gases on the periodic table. Web so halogens tend to gain one electron to form a monovalent anion or negatively charged ion and achieve the stable noble gas configuration. Web halogens in alkali metals are likely.
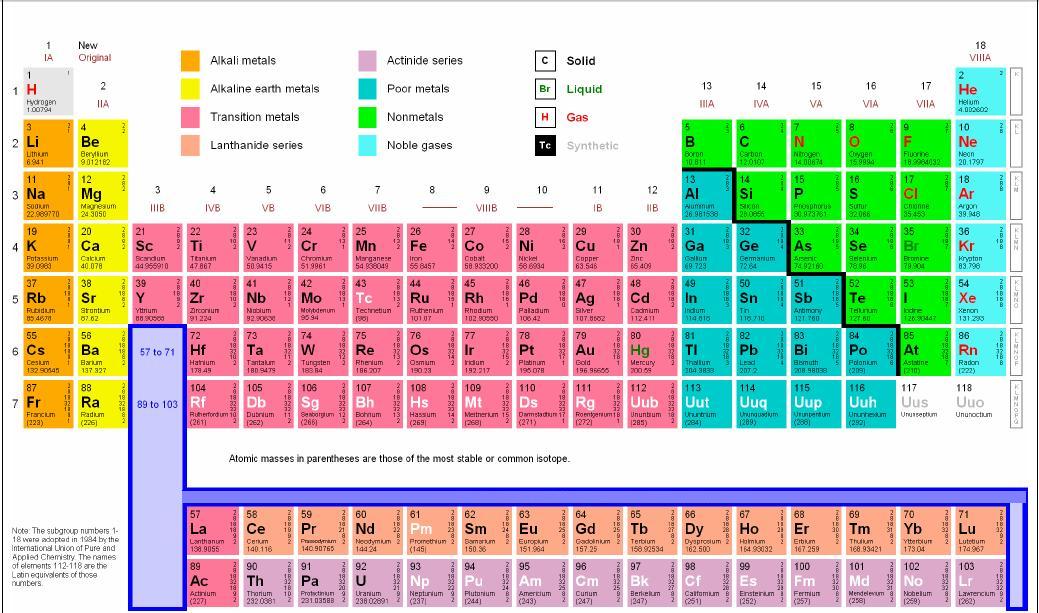
Periodic Table Alkali Metals Halogens Noble Gases Periodic Table Timeline
Web halogens such as chlorine, bromine and iodine have properties that enable them to react with other elements to form important salts such as sodium chloride, also. Web the electrolysis is carried out in an argon atmosphere rather than the nitrogen atmosphere typically used for substances that are highly reactive with o 2 and water because li. Web in the.
Why Halogens Are So Reactive slidesharedocs
Web ions made from alkaline earth metals, the second group on the periodic table, have a 2+ charge. Web most common nonmetallic substances such as halogens, halogen acids, sulfur, and phosphorus react with the alkali metals. Web in the modern iupac nomenclature, this group is known as group (xvii) or group (vii). Most binary halides are ionic. Halogen group (group.
Why are halogens and alkali metals likely to form ions quizlet? Book Vea
Well, the answer lies in the balance show. Web most common nonmetallic substances such as halogens, halogen acids, sulfur, and phosphorus react with the alkali metals. The alkali metals react with the nonmetals in group viia (f 2, cl 2, br 2, i 2, and at 2) to form ionic compounds or salts. The halogens are located on the left.
Solved 53.9 Resources Hint СІ Question 12 of 22 > Metals
Web reactions of alkali metals with group viia. Less because i’m putting a couple things i know together to get the explanation. Expert solution step by step solved in 2 steps see solution check. So, as you know, alkaline metals are group one, and they all have. Web they react aggressively with the halogens to form the alkali metal halides,.
Web When Do Chemical Bonds Form?
Halogen group (group 17) trends. Web concept explainers question why are halogens and alkali metals likely to form ions? Why are halogens and alkali metals likely to form ions? The halogens are located on the left of the noble gases on the periodic table.
Web They React Aggressively With The Halogens To Form The Alkali Metal Halides, Which Are White Ionic Crystalline Compounds That Are All Soluble In Water Except Lithium Fluoride (Li F).
Well, the answer lies in the balance show. They have a low ionization energy, due to them. Web ions made from alkaline earth metals, the second group on the periodic table, have a 2+ charge. [4] the word halogen means salt former or salt maker.
Web Halogens In Alkali Metals Are Likely To Form Ions Because Their Ionization Energy Is Very Low Because They Only Need To Lose Or Gain One Electron.
Web in the modern iupac nomenclature, this group is known as group (xvii) or group (vii). When they share or transfer electrons. Web the electrolysis is carried out in an argon atmosphere rather than the nitrogen atmosphere typically used for substances that are highly reactive with o 2 and water because li. Web when the alkali metals react with the different halogens (group 7 of the periodic table), the group of compounds formed are known as the alkali metals halides.
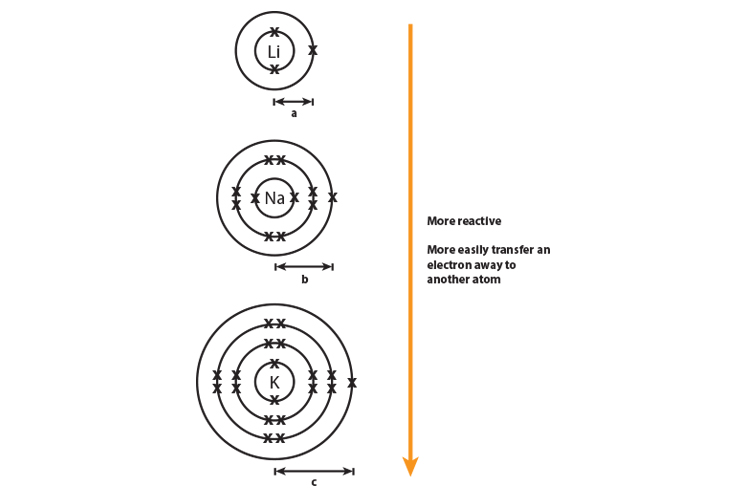
Web Halogens Need To Gain Only One Electron And Alkali Metals Need To Lose One Electron In Order To Reach The Nearest Noble Gas Configuration And Become More Stable.
Web most common nonmetallic substances such as halogens, halogen acids, sulfur, and phosphorus react with the alkali metals. Web atomic and physical properties of halogens. Web halogens such as chlorine, bromine and iodine have properties that enable them to react with other elements to form important salts such as sodium chloride, also. So, as you know, alkaline metals are group one, and they all have.