How Many Bonds Does Hydrogen Form
How Many Bonds Does Hydrogen Form - What is called the number of bonds an atom can. Web hydrogen bond strengths range from 4 kj to 50 kj per mole of hydrogen bonds. Web hydrogen is nonmetallic (except when it becomes metallic at extremely high pressures) and readily forms a single covalent bond with most nonmetallic elements, forming. Web hydrogen bonds form between the hydrogen atom of one water molecule and the lone pair on the oxygen atom of another molecule. Hydrogen bonds are extremely important in biology, as they are the reason for the structure of dna and its properties. Intramolecular hydrogen bonding intermolecular hydrogen bonding now understand. In this question, we need to determine the. This leads to the hexagonal cage structure of crystalline ice. Web nov 7, 2016. Web hydrogen forms weak bonds between molecules, latching onto adjacent oxygen, nitrogen or fluorine atoms.
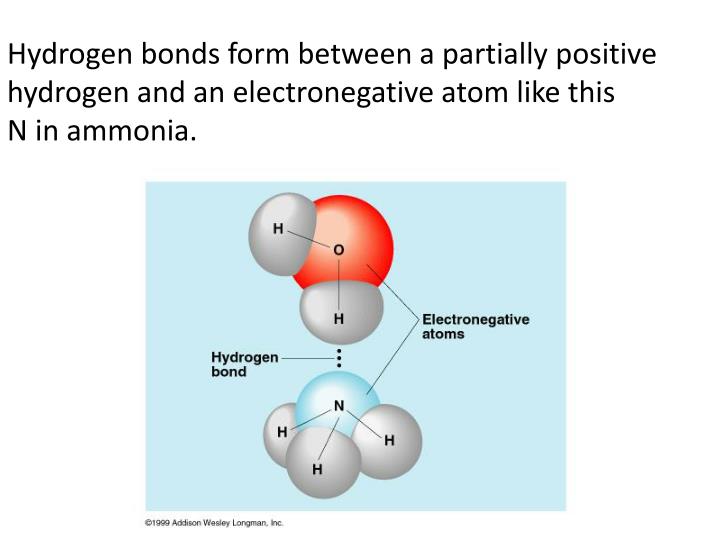
This leads to the hexagonal cage structure of crystalline ice. It's these hydrogen bonds that give water many of its properties. Web hydrogen bonding in dna. Hydrogen bonds are extremely important in biology, as they are the reason for the structure of dna and its properties. Web any molecule which has a hydrogen atom attached directly to an oxygen or a nitrogen is capable of hydrogen bonding. Web hydrogen is nonmetallic (except when it becomes metallic at extremely high pressures) and readily forms a single covalent bond with most nonmetallic elements, forming. Such molecules will always have higher. Web a hydrogen atom will typically form two covalent bonds because hydrogen has two electrons to share in a bond. Web hydrogen bonds form between the hydrogen atom of one water molecule and the lone pair on the oxygen atom of another molecule. In this question, we need to determine the.
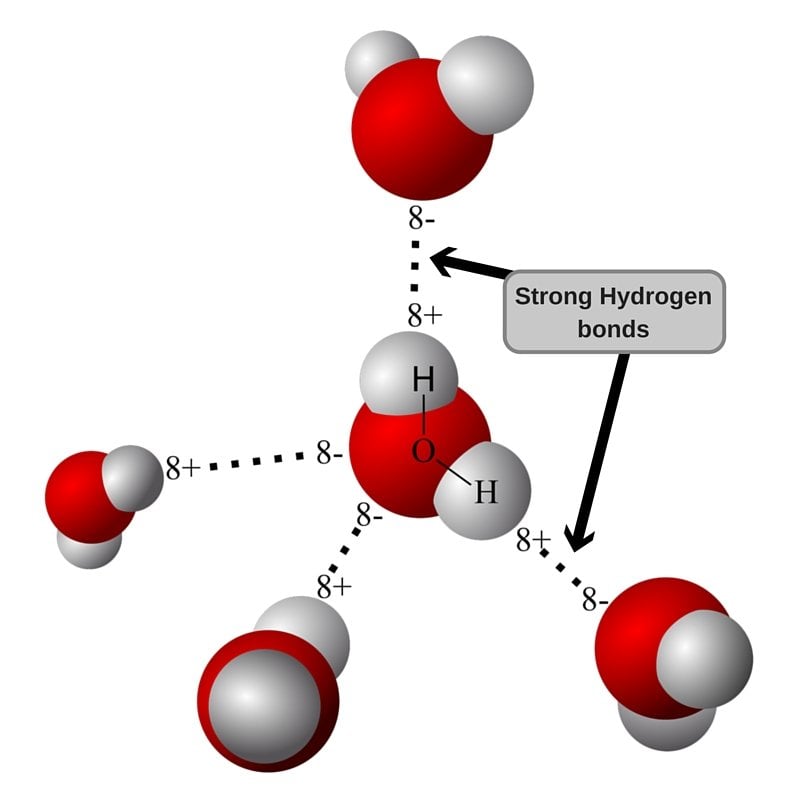
Web hydrogen is nonmetallic (except when it becomes metallic at extremely high pressures) and readily forms a single covalent bond with most nonmetallic elements, forming. Web nov 7, 2016. Web hydrogen forms weak bonds between molecules, latching onto adjacent oxygen, nitrogen or fluorine atoms. Web there are two types of hydrogen bondings which are given below. Web notice that each water molecule can potentially form four hydrogen bonds with surrounding water molecules: Using pauling's scale—c (2.55) and h. What is called the number of bonds an atom can. This leads to the hexagonal cage structure of crystalline ice. Hydrogen bonds are extremely important in biology, as they are the reason for the structure of dna and its properties. Web hydrogen bonding in dna.
Properties of Water Presentation Biology
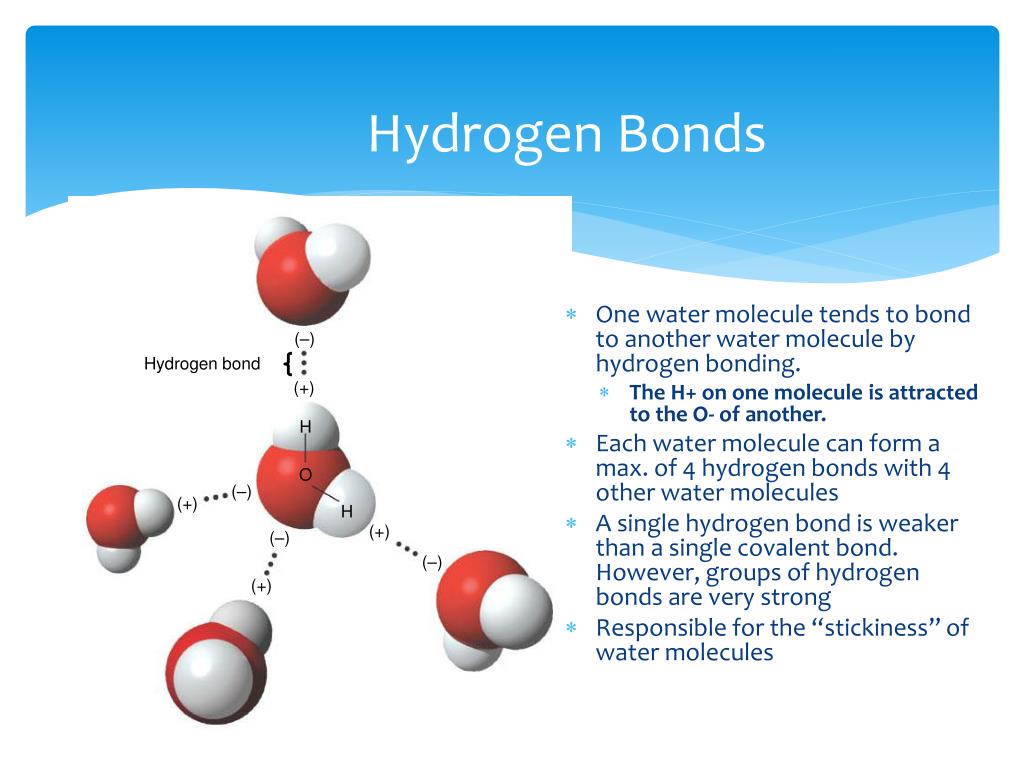
Web hydrogen bonds form between the hydrogen atom of one water molecule and the lone pair on the oxygen atom of another molecule. Web nov 7, 2016. Web any molecule which has a hydrogen atom attached directly to an oxygen or a nitrogen is capable of hydrogen bonding. Web hydrogen forms weak bonds between molecules, latching onto adjacent oxygen, nitrogen.
2.2 Chemical Bonds Anatomy & Physiology
Web any molecule which has a hydrogen atom attached directly to an oxygen or a nitrogen is capable of hydrogen bonding. In this question, we need to determine the. Web nov 7, 2016. This leads to the hexagonal cage structure of crystalline ice. Web a hydrogen atom will typically form two covalent bonds because hydrogen has two electrons to share.
How many hydrogen bonds a water molecule can form Hydrogen Bonding in
Web nov 7, 2016. Web hydrogen is nonmetallic (except when it becomes metallic at extremely high pressures) and readily forms a single covalent bond with most nonmetallic elements, forming. Web notice that each water molecule can potentially form four hydrogen bonds with surrounding water molecules: Web hydrogen bond strengths range from 4 kj to 50 kj per mole of hydrogen.
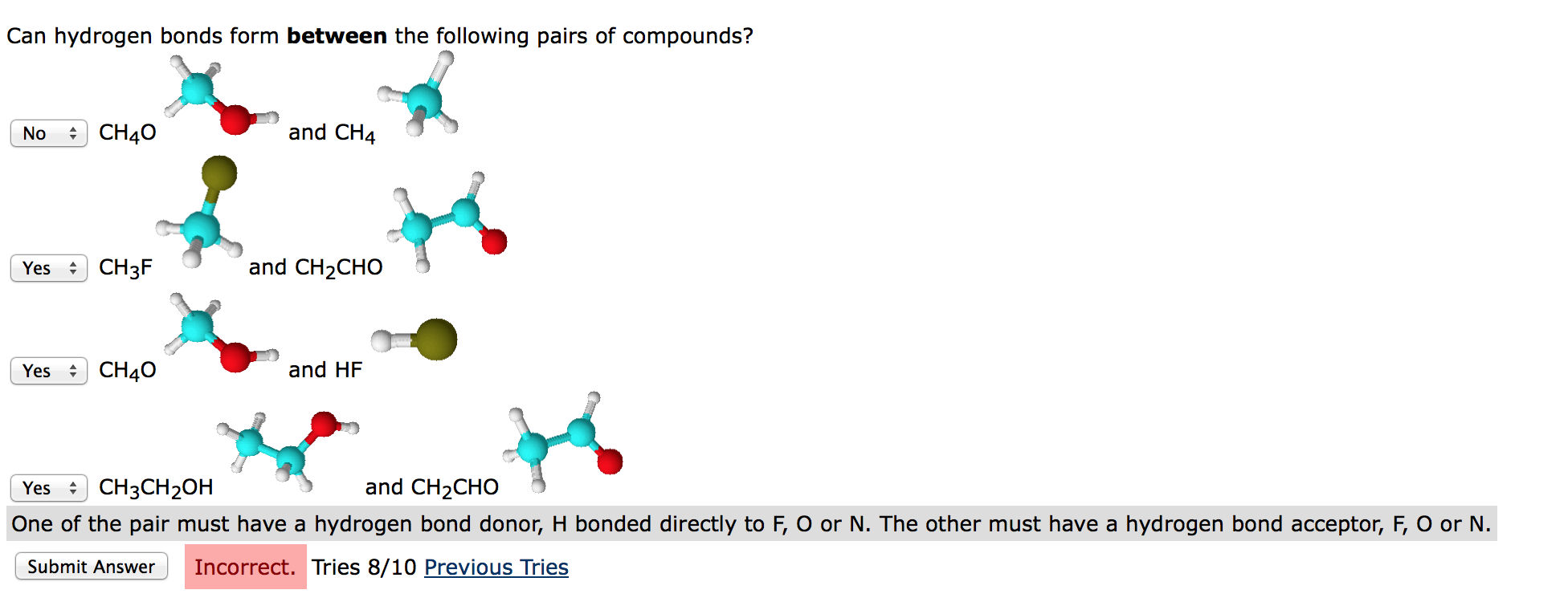
Solved Can hydrogen bonds form between the following pairs
Web hydrogen is nonmetallic (except when it becomes metallic at extremely high pressures) and readily forms a single covalent bond with most nonmetallic elements, forming. Thus one hydrogen atom will only bond once. Since hydrogen has only one valence electron, it will only bond once. In this question, we need to determine the. Web a hydrogen atom will typically form.
PPT Chemistry—A Quick Review PowerPoint Presentation ID3103671
Web a hydrogen atom will typically form two covalent bonds because hydrogen has two electrons to share in a bond. Web nov 7, 2016. Web hydrogen bonding in dna. Web hydrogen is nonmetallic (except when it becomes metallic at extremely high pressures) and readily forms a single covalent bond with most nonmetallic elements, forming. Using pauling's scale—c (2.55) and h.
PPT Properties of Water PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID
Web notice that each water molecule can potentially form four hydrogen bonds with surrounding water molecules: Intramolecular hydrogen bonding intermolecular hydrogen bonding now understand. In this question, we need to determine the. Hydrogen bonds are extremely important in biology, as they are the reason for the structure of dna and its properties. Web a hydrogen atom will typically form two.
how many bonds does sulfur form
Hydrogen bonds are extremely important in biology, as they are the reason for the structure of dna and its properties. Such molecules will always have higher. Web nov 7, 2016. Web notice that each water molecule can potentially form four hydrogen bonds with surrounding water molecules: Web hydrogen is nonmetallic (except when it becomes metallic at extremely high pressures) and.
Bonds That Hold Water Molecules Together / Intermolecular Forces
Web any molecule which has a hydrogen atom attached directly to an oxygen or a nitrogen is capable of hydrogen bonding. Using pauling's scale—c (2.55) and h. Web notice that each water molecule can potentially form four hydrogen bonds with surrounding water molecules: Since hydrogen has only one valence electron, it will only bond once. What is called the number.
Why Do Fingers/Hands Stick To Ice? » Science ABC
Two with the hydrogen atoms and two with the with. This leads to the hexagonal cage structure of crystalline ice. Web hydrogen forms weak bonds between molecules, latching onto adjacent oxygen, nitrogen or fluorine atoms. Using pauling's scale—c (2.55) and h. In this question, we need to determine the.
Hydrogen bonds YouTube
Web hydrogen bonds form between the hydrogen atom of one water molecule and the lone pair on the oxygen atom of another molecule. Web hydrogen is nonmetallic (except when it becomes metallic at extremely high pressures) and readily forms a single covalent bond with most nonmetallic elements, forming. Such molecules will always have higher. Hydrogen bonds are extremely important in.
This Leads To The Hexagonal Cage Structure Of Crystalline Ice.
Intramolecular hydrogen bonding intermolecular hydrogen bonding now understand. Web hydrogen forms weak bonds between molecules, latching onto adjacent oxygen, nitrogen or fluorine atoms. Hydrogen bonds are extremely important in biology, as they are the reason for the structure of dna and its properties. Web hydrogen bond strengths range from 4 kj to 50 kj per mole of hydrogen bonds.
Such Molecules Will Always Have Higher.
Web a hydrogen atom will typically form two covalent bonds because hydrogen has two electrons to share in a bond. What is called the number of bonds an atom can. Two with the hydrogen atoms and two with the with. Web notice that each water molecule can potentially form four hydrogen bonds with surrounding water molecules:
It's These Hydrogen Bonds That Give Water Many Of Its Properties.
Web any molecule which has a hydrogen atom attached directly to an oxygen or a nitrogen is capable of hydrogen bonding. Web hydrogen bonds form between the hydrogen atom of one water molecule and the lone pair on the oxygen atom of another molecule. Web nov 7, 2016. Thus one hydrogen atom will only bond once.
Since Hydrogen Has Only One Valence Electron, It Will Only Bond Once.
Web hydrogen bonding in dna. Using pauling's scale—c (2.55) and h. Web there are two types of hydrogen bondings which are given below. In this question, we need to determine the.
.PNG)